 Image source: Generated by AI
Image source: Generated by AI
Artificial intelligence has also felt unprecedented enthusiasm in the medical community.
“We must embrace AI.”At several recent events where medical AI models were released, clinical experts said this.
After the rapid iteration from Doubao to Kimi to DeepSeek, even China’s top medical experts feel “at a loss.” Ning Guang, academician of China Academy of Engineering and president of Ruijin Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, once publicly stated that the whole society is being reshaped by AI and big models. If we don’t embrace AI, we will become an outsider.
Can AI really be a doctor? Three or four years ago, this was considered a distant thing, but now it has come true. With the release of DeepSeek, an unprecedented sense of urgency swept the entire medical community.Public hospitals, which have always been cautious about AI, have also undergone a 180-degree transformation.
According to industry statistics, in the short two or three weeks after the Spring Festival, at least 92 China hospitals have officially announced or reported by media access to DeepSeek and completed localized deployments. This number is still rising. Judging from the specific list, well-known hospitals in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou, and top-A hospitals in various provinces and cities are among them.
At the same time, AI medical companies connected to DeepSeek are also providing tailor-made services such as AI mid-station construction that integrates multiple models for major hospitals. At the regulatory level, more radical cities have health commissions and medical insurance bureaus connected to this model.
“We are busy with business, and we are currently on business trips in various places, and we are so busy that we want to vomit.” A medical AI company entrepreneur told Hu Smell.
Compared with previous AI models, DeepSeek has brought a lot of shock to the relatively traditional, rigorous and conservative medical industry.
Not long ago, a doctor broke the news on social platforms that during the medical visit, the patient used DeepSeek to question his diagnosis. The doctor was very angry, but when he went back to check, the guide was updated. His diagnosis was outdated. This made him feel that “the sky is falling”, and it also made many grassroots doctors feel that the sky is falling.
Judging from DeepSeek’s more performance in the medical field, this is only the beginning.
01. DeepSeek is coming fiercely
DeepSeek is the biggest outlet since the beginning of the New Year. Medical-related institutions and individuals all want to do something in it. DeepSeek’s performance is indeed remarkable, and it has even penetrated into the very core surgical scenarios in medical care.
“Through multimodal assessment and technical empowerment, we see the possibility of cure.”
This is what Xiong Wei, director of the Department of Urology at the People’s Hospital of Sichuan Province, said in an interview with cover news. Prior to this, Xiong Wei and his team completed radical surgery for “right renal pelvis cancer with inferior vena cava cancer” on an 82-year-old patient with refractory disease. This is regarded as an operation that crosses the “forbidden zone of life”.
According to public information, this patient’s condition is very dangerous. The cancer thrombus completely blocked his inferior vena cava, and there is still a risk of edema and thrombosis in both lower limbs. In the past, conservative treatment could only be used. Because of his advanced age and complex condition, if surgery is performed, his cardiopulmonary function cannot tolerate long surgery, fatal bleeding occurs during the operation, and complications such as acute renal function damage occur after surgery.
For complex situations, DeepSeek not only provides a personalized perioperative management plan, covering risk warning, medication decisions, rehabilitation paths and complication radar, but also locates the location of lesions and blood vessels in real time during the procedure, reducing bleeding and other issues, combined with high-precision CT imaging three-dimensional construction of “digital vasculature” and other technologies, the operation finally took 4 hours to complete successfully.
Doctors commented that this series of new technologies is equivalent to equipping the team with a “risk perspective.”
In more medical institutions, DeepSeek is used in administrative management, existing AI-assisted diagnosis and other fields to improve efficiency and accuracy.
According to the director of the Information and Data Department of a hospital in Changsha City that uses DeepSeek to assist in reading, with DeepSeek’s support, the reading time of the AI-assisted diagnosis of pulmonary nodules system has been shortened by 40%, the identification rate of small lesions has been increased by 25%, and the accuracy rate has reached more than 95%. In the field of gastroscopy, the consistency rate between the AI system’s prediction and the “gold standard” pathological examination results has also reached 96%.
For more sub-health people, there are already “AI doctors” who can serve them 24 hours a day. For example, the “Urology AI Doctor”(virtual digital doctor) launched by the Department of Urology at the Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University can respond to patient consultations at any time, complete more than 80% of standardized questions and answers, and can also customize personalized health management plans for patients.
“Using AI technology or large models to do image analysis, the comprehensiveness, accuracy and speed are completely unmatched by artificial image analysis.”Some clinical experts pointed out at the press conference of the medical model.
The industry believes that large-scale access to the AI model by medical institutions will be of great help to improve diagnosis and treatment efficiency and quality. From an industry perspective, this will also point to a new round of rapid changes in the medical industry.
From: Visual China
02. It will be too late if I don’t embrace AI
To a certain extent, the medical community is already accepting AI. DeepSeek, a large model with extremely high cost performance, has directly condensed the landing process. This will further intensify competition in the medical market.
In hospitals, many tasks are done manually by doctors, which is very time-consuming and laborious. The pathology department, a department known as the “pearl on the crown of medicine”, is as boring and stressful as a doctor’s work, even as “screwing” in a factory.
In the past two or three years, with the rapid development of AI technology, clinicians have long had a deep understanding of AI capabilities.“Human energy is limited, and AI can pull out endless databases.”Shen Longhai, deputy director of the First Oncology Ward of Baoshihua Hospital in Liaoyou and chairman of the Panjin Oilfield Branch of Jiusan Society, told Hu Xian that AI-assisted diagnosis and digital people play an important role in daily work and science popularization.
A doctor who has worked in the radiation (treatment) department of the hospital for many years also told Hu Xian that ten years ago, they needed to outline the contours of the heart, lungs and other organs on CT images little by little on the computer. Their eyes were dry, their fingers were sour, and the image was still crooked. At that time, she felt that “it was stupid to manually hold a mouse to draw and outline on a computer, and that the drawing should be recognized (automatically).”
Now this goal has been achieved. “60 seconds! It was generated with one click from the first hour or two of work.” The above-mentioned doctor told Hu Xian that although the doctor still needed to make some modifications, it was already very convenient.“I have seen the rapid changes in AI-assisted medicine.”
Now, the time for patients to report pathology in county-level hospitals has also been shortened from at least 3 days to 24 hours.
The arrival of AI frees doctors from heavy, repetitive labor and can do some details better than humans.
Shen Longhai took the “drawing the target area” in tumor radiotherapy, that is, the work of determining the radiotherapy site, as an example and explained to Hu Xian that it turns out that this work takes at least 6 hours to complete, and it is difficult to draw on a computer with a mouse. Control the graphics, after using AI, not only is the speed faster, but the graphics are more round and smooth.
In the more core surgical field, surgical machines loaded with new technologies such as AI can long control the error to within 0.1 mm, overcoming the effect of hand tremors of human doctors, and reducing postoperative complications. According to public reports, the incidence of anastomotic leakage during urethral reconstruction has dropped from 8% to 2%.
The national level is also actively promoting the implementation of intelligent assistive tools such as AI in the medical field. In November last year, the National Health Commission and other departments jointly issued a guidance document, announcing 84 “artificial intelligence +” applications in the fields of medical services and grassroots public health. Application scenarios.
Not long ago, the National Natural Science Foundation of China announced that among the projects that can apply for project funds, there are also many artificial intelligence-related projects, covering myocardial infarction warning, rare disease diagnosis, immunity decoding, etc. More directly, the latest three-level hospital review requirements also include the level of medical informatization. For large hospitals, informatization transformation has become a critical need.
In addition to the technological progress and policy guidance of AI itself, the living situation of medical institutions also forces them to seek change.
According to Sanlian Life Weekly, in 2024, more than 1200 of the bankruptcy declaration information published on relevant websites were related to hospitals. This number is more than twice that of 2022 and about 400 more than in 2023. Among these hospitals, there are not only private hospitals but also public hospitals.
According to industry analysts, this is mainly related to the large-scale expansion and upgrading of public hospitals and the development path of increasing the number of patients, resulting in a surge in costs and lagging hospital revenue growth. This situation deteriorated sharply after medical insurance funds shifted from pay-by-project to pay-by-disease.
Hospital revenue from medical insurance is declining,Forcing hospitals to transform from extensive development models to refined managementIf it cannot be changed in time, it is very likely that the flow of funds will break.
An article studying the Affiliated Hospital of Jiaying College of Medicine in Guangdong Province (Second Class Public Hospital), which went bankrupt last year, pointed out that from 2022 to 2023, the hospital’s medical revenue exceeded 75 million yuan, but 120 million yuan was invested in the expansion. In the new situation, the funding gap gave it a fatal blow.
Looking at the new policy trend, medical insurance funds are gradually shifting to skipping public hospitals and settling accounts directly with drug and device companies, which will also pose a greater challenge to the cash flow of public hospitals.
For hospital directors who are at a critical juncture of life and death, any new tool that can effectively improve management levels and improve diagnosis and treatment efficiency is a “life-saving straw.”

From: Visual China
03. How will DeepSeek affect the medical landscape?
Long-standing problems in the medical industry, including insufficient staff, inefficiency, and excessive diagnosis and treatment, have made both inside and outside the industry look forward to relying on new technologies to solve them.
Unfortunately, what AI can do is still very limited.
Shen Longhai told Hu Xian that although AI-assisted diagnosis and treatment can do many things, it is still impossible to complete tasks independently in the face of complex human conditions.For example, when the above-mentioned radiotherapy target delineation is encountered, once special circumstances are encountered, such as a patient with vascular malformations or intestinal malformations, the AI delineation of organs will be incorrectly identified. If there is no doctor’s correction, normal organs may be endangered.
“AI still cannot replace people in many aspects.” Shen Longhai said to Hu Xian. In addition to the ability to be improved, whether AI can really empathize with people’s experiences has also been questioned by the industry. Even if DeepSeek even surpasses humans in terms of thinking ability and cannot give people spiritual support in science popularization, it is difficult to formulate personalized treatment plans based on comprehensive considerations of patients ‘financial ability, physical condition and other aspects.
“People have temperature, but machines have no temperature.” Shen Longhai said.
Moreover, the complexity of medical treatment lies in that it is difficult for ordinary people to accurately describe medical history, symptoms, etc. to AI. If the diagnosis or treatment plan is made according to the wrong information provided by the patient, it is likely to lead to a sharp deterioration of the condition.
In addition, the addition of AI has made medical examinations more sensitive and has also caused the industry to worry about new “overdiagnosis and treatment.” In fact, after AI has been connected to CT in the past few years, the detection rate of lung nodules has been rising all the way, causing more and more people to fall into anxiety.
From the perspective of the industry structure, technology alone may not be able to achieve the goal of graded diagnosis and treatment and strengthening the grassroots.
Although the most frequently mentioned vision in the AI+ medical field is to use new technologies to improve grassroots medical levels and achieve hierarchical diagnosis and treatment, judging from the current situation, new technologies such as AI are opening up large hospitals and primary medical institutions more significantly. gap.
In fact, medical institutions have long had a demand for new technologies, but they have not yet been implemented. In addition to the technology that has not reached a level that satisfies them, economic considerations are also one of them.This is also one of the fundamental reasons why DeepSeek, which is cost-effective, quickly captured so many hospitals.
According to the data released by DeepSeek’s official website, the input and output cost of DeepSeek-R1 is less than a fraction of that of the slightly more capable GPT4-o1. In the case of a cache hit, the input token cost of DeepSeek-R1 is 1 yuan/million tokens, which is only 1.8% of the O1 charging standard and less than one-tenth of the O1-mimi with worse capabilities. Moreover, this price is still decreasing. According to the latest news, from 0:30 to 8:30 every day Beijing time, the API cost of DeepSeek-R1 can be reduced by 75%!
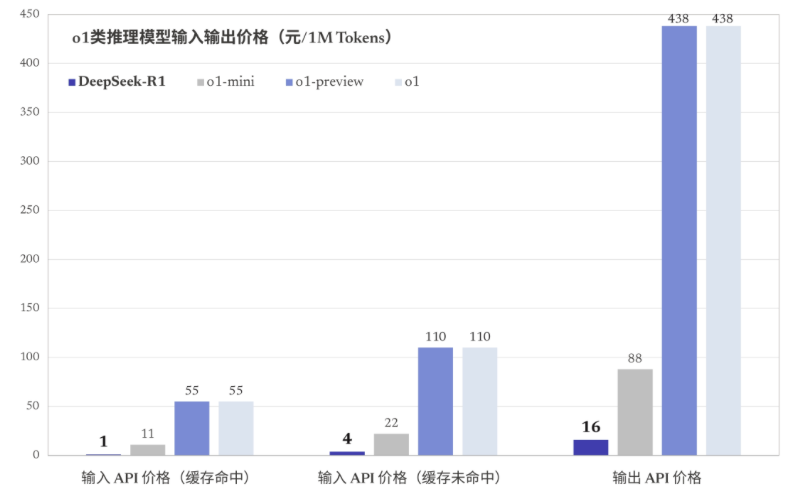
DeepSeek-R1 API input and output costs. From: DeepSeek official website
In terms of other expenses, some industry insiders have calculated that if it is just local testing and performing some basic natural language model tasks, such as translation, multiple rounds of conversations, etc., the hardware cost of deploying DeepSeek in hospitals can be as low as tens of thousands of yuan. The high configuration cost does not exceed one million yuan. If it is a professional field with higher precision, it can also be as low as more than 4 million yuan.
In this way, many regional leading hospitals will have the opportunity to locally deploy technologically advanced AI models.
Despite this, judging from hospital official announcements, many hospitals still use DeepSeek to help doctors complete basic work areas such as asking patients about symptoms and medical history, reviewing data, and writing cases. It can indeed improve efficiency, but it does not fully utilize DeepSeek’s potential.
For primary medical institutions, whether they have the strength and motivation to introduce this technology is even more doubtful.
On the other side of the coin, the needs of top medical institutions, experts and scholars are more complex, and they are using AI to push up the threshold and ceiling of diagnosis and treatment services.
Since February, Beijing Children’s Hospital, Shanghai Ruijin Hospital, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, etc. have all pushed professional large models developed in cooperation with technology companies to the public. These large models can be used in consultations; they can help doctors read complex pathology reports with an accuracy of more than 90%; and their professional knowledge reserves even reach the level of full professors.
The promotion of these large models will undoubtedly increase the capabilities of more medical institutions to a new level. Top medical institutions will rely on AI to form a new medical model, and the pinnacle of disease treatment will move from specialization to personalization and to precision medicine.
This is a future worth looking forward to for patients and may be a reshuffle for the medical industry.
What cannot be ignored is that the technical requirements and costs behind it will be much higher than Pratt & Whitney’s DeepSeek. It can be seen that when Xiangya Hospital of Central South University deployed DeepSeek locally, it introduced a number of domestic top large models, as well as a database built in cooperation with technology companies such as Yidu Technology over the past six years.
This means that under the screening of the two mountains of data and funds, top medical institutions will move farther and farther with the help of AI, and leading hospitals in various regions will also have better development, forming a more stable multi-regional center pattern. The gap between primary medical institutions and them will be even wider. In addition to some institutions that can be included in the medical consortium, more primary medical institutions that lack characteristics and talents are likely to become places for prescribing drugs and infusions, or even go bankrupt.
If primary medical institutions are to benefit from technological progress, more institutional guarantees and policy guidance are bound to be needed.
Recently, amid the rise of AI, regulatory authorities have reiterated the strict prohibition of AI prescribing. In addition to medication safety considerations, this also objectively stabilizes the lifeline of primary medical institutions. However, this is the bottom line. How to make AI truly promote the healthy development of the medical industry still needs more discussion.
DeepSeek is not a “savior”.
However, from an optimistic perspective, with the help of DeepSeek’s fire, the medical industry has accepted AI on a wider scale. Before products that can truly solve medical pain points are available, as industry insiders say, make full preparations-including building a high-quality, professional database may be the top priority.



