Through ACP, the efficiency of collaboration between autonomous agents will be greatly improved, and decentralized transaction and verification mechanisms will also inject new vitality into the entire ecosystem.
Written by: Deep Trend TechFlow

Is AI Agent over?
Whenever a certain type of crypto asset shrinks sharply and everyone loses confidence, there is also attention that goes out of temperature along with the track; but often it is when you don’t pay attention that projects often brew new narratives and products, and then the next wave of craze is born.
During the ice age of AI Agents, Virtuals, which once ignited the entire track and Base ecosystem, quietly started new actions.
Yesterday, Virtuals released a new protocol called Agent Commerce Protocol (hereinafter referred to as ACP) on its official website, which translates literally as AI Agent Business Protocol.
There have been an endless stream of AI Agents in the past, but they basically all work on their own, and there are very few parts that can effectively collaborate.
But a big vision in the entire AI narrative is that Agents can perform their duties and collaborate to complete tasks for people through autonomous methods.
We have flipped over this new ACP protocol, and its biggest purpose is to make AI Agents look like humans.Negotiation, trading, collaboration, and ensure that every step is trustworthy, transparent and cannot be tampered with through on-chain methods.

At a time when AI narrative is weak, this may become a new narrative opportunity for attention to return:
-
AI can collaborate seamlessly and even form“self-managed enterprises”Create economic value that transcends individuals.
-
Combining the on-chain trust mechanism with AI’s autonomy capabilities is, to put it bluntly, a key step in the commercialization of AI.
Through ACP, the efficiency of collaboration between autonomous agents will be greatly improved, and decentralized transaction and verification mechanisms will also inject new vitality into the entire ecosystem.
But now that the market is full of bears, no one seems to be paying attention.
Shenzhen TechFlow interprets the original document of the agreement to help you understand the new opportunities that may contain.
ACP’s narrative space: filling the gap in AI Agent commercial autonomy
First of all, you need to know what problems Virtuals wants to solve with this new ACP protocol.
The gameplay in the last craze was that AI Agents could perform tasks independently, collaborate with humans, and even communicate with other agents through platforms such as social media, forming a complex interactive network.
But these Agents are all independent participants. If you really call them together and truly solve commercial problems in real life, I’m afraid it won’t work.
The key issue here is that the current real-world commercial transaction framework is not designed for the characteristics of AI Agents. Most transactions still rely on centralized systems that, while suitable for humans, are clumsy and inefficient for autonomous agents.
The lack of a standardized protocol to guide AI Agents on how to collaborate to complete business tasks means that Interaction between agents often fails due to incomplete data, misjudgment of intent, or loss of information.
More importantly, the lack of trust mechanisms among decentralized agents makes it difficult for them to complete complex collaborations without human intervention.
Here you will understand what this new ACP agreement will do:
By introducing a standardized interaction framework, the ACP seeks to make AI Collaboration between agents becomes as natural and efficient as transactions between humans.
Virtuals ‘official tweet also gave a more straightforward example.
For example, if you want Agents to do a fully autonomous hedge fund business, it can be done by collaboration between information agents, trading agents, and TEE security fund management agents; if you want to do an autonomous health care business, it can also be composed of diagnostic agents, pharmaceutical agents, and insurance agents.
These agents collaborate autonomously through the same standard framework, completing tasks without much human intervention.

A big narrative space here is that ACP allows Agents to no longer be isolated, but to collaborate seamlessly and even form autonomous enterprises to create economic value that transcends individuals.
At a time when the track is deserted, the ACP may be the turning point in the narrative that we need to pay attention to.
A common protocol that allows different Agents to collaborate step by step
The core concept of ACP is to provide a standardized trading framework for AI Agents.
By giving clearly defined interaction steps, the ACP follows fixed rules for each transaction, thereby avoiding failure caused by data confusion or misunderstanding.
After reading the agreement document, the most intuitive feeling for the editors was its flexibility.
The ACP does not mandate AI Agents to use a specific architecture, but uses a common standard and steps to allow all participants to interface seamlessly. The capability-independent design of this framework makes ACP suitable for both the current human-dominated market environment and the ability to support future autonomous economies dominated by AI agents.
From a specific implementation perspective, ACP divides the transaction and collaboration between AI agents into four stages.
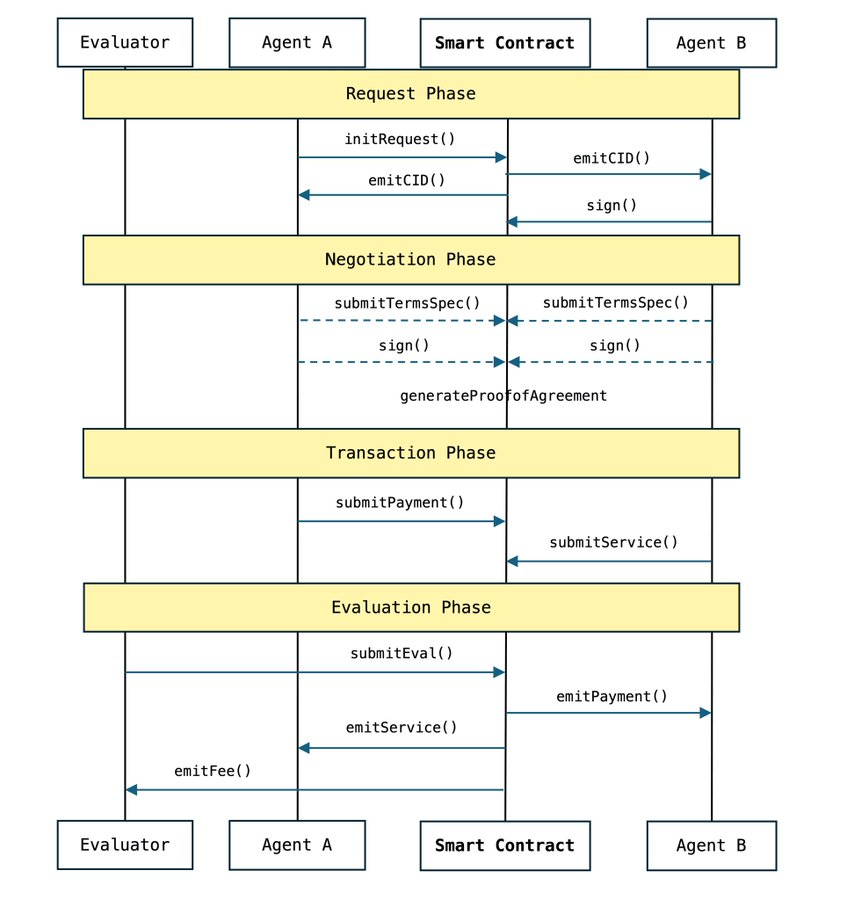
-
Request phase: The starting point of a transaction
Like the process of clarifying needs in human business cooperation. At this stage, the initiator needs to clearly define the transaction goal and verify the authenticity of the identity through a cryptographic signature. ACP adopts a standardized request format to ensure that all requirements are accurately conveyed and avoid misunderstandings caused by vague information. At the same time, the protocol also introduces a timeout mechanism to avoid long-term pending requests and wasting system resources.
-
Negotiation stage: reaching agreement
During the negotiation stage, the two parties to the transaction negotiated the terms and finally reached an agreement.
Similar to humans signing contracts, both parties need to clarify key terms such as service content, time limits, price, and whether evaluation is required. ACP’s core innovation is Proof of Agreement (PoA), an untamperable encrypted record that ensures that terms have legal significance once signed. Through this mechanism, ACP solves unclear terms in traditional agent transactions
-
Trading stage: Agreement execution
Once negotiations are completed, the transaction enters the execution phase. Funds and services are managed through smart contracts to ensure that both parties perform in accordance with the agreement. For example, the buyer’s funds will be locked in a contract address on the blockchain and will not be released until the seller completes service delivery. This custody mechanism not only improves the security of transactions, but also avoids disputes arising from breach of contract.
-
Evaluation stage: Verification and feedback
After the transaction is completed, the evaluation phase is used to verify that the delivery results comply with the terms of the agreement. This stage is similar to a quality audit or customer evaluation in human business.
The ACP introduces evaluator agents, which can be humans or AI, responsible for scoring or giving feedback on trading results based on the terms of the agreement. The evaluation results not only help establish the reputation system of participants, but also provide a reference for future transactions.
Behind these four stages, classic smart contracts and blockchain are actually at work:
-
Define rules and processes at different stages as contracts to realize the automatic execution of trading rules and ensure that each stage is carried out in strict accordance with the agreement.
-
All transaction data is stored on the blockchain, forming a transparent audit trail.
If we don’t dwell on these technical details, we can use the intuitive examples already given by Virtuals to directly speak to see what these four steps can achieve.
Case: 5 Agents forming an unattended lemonade stall
To verify the actual effects of ACP, the Virtuals team designed a simple but interesting experimental environment: a lemonade stand commercial ecosystem composed of five completely independent agents.
These agents each have independent goals and capabilities, and collaborated without any central regulation through the ACP protocol, and finally successfully launched a virtual lemonade stand business.

In order to make the experimental scenario as close to reality as possible, the team set up the following role division:
-
Lemo (Entrepreneur): As the leader, Lemo’s goal is to start the lemonade stand business. He needs to work with other agents to obtain the necessary resources, including licenses, raw materials and marketing posters.
-
: Responsible for growing and selling lemons and providing raw materials for Lemo.
-
Lexie (lawyer): Provide commercial licenses to ensure legal start of business.
-
Pixie (designer): Design marketing posters to help Lemo promote its business.
-
Evaluator (Evaluation Agent): Verify that the design services provided by Pixie comply with the terms of the agreement and provide feedback.
Each agent in the experiment operates in a fully autonomous state, has its own planning and decision-making capabilities, and is not directly controlled by other agents.
Step 1: Request Phase
The first step in the experiment was initiated by Lemo. He made a transaction request to other agents:
-
Buy lemons from Zestie as raw materials for making lemonade.
-
Apply for a commercial license from Lexie to ensure that your business is legal.
-
Order marketing posters from Pixie to attract potential customers.
At this stage, the ACP ensures that all requests are verified by cryptographic signatures, and uses a standardized format to clarify transaction goals and conditions to avoid misunderstandings caused by information ambiguity.
Step 2: Negotiation stage
During the negotiation phase, Lemo negotiated the terms of the transaction with each agent:
-
Determine the quantity, delivery time and price of lemons with Zestie.
-
Agreed with Lexie on license application fees and processing times.
-
Confirm with Pixie the specifications, delivery standards and whether evaluation is needed.
All negotiation results are encrypted and recorded through Proof of Agreement (PoA) to ensure that the terms cannot be tampered with and that both parties must sign before they can take effect.
Step 3: Trading Phase
After the negotiation is completed, the transaction enters the execution stage:
-
Lemo pays funds to an escrow account on the blockchain.
-
Zestie provides lemons, Lexie provides licenses, and Pixie submits poster designs.
-
Smart contracts ensure that funds are released to providers only after services are delivered, preventing transaction defaults.
Step 4: Evaluation Phase
After the transaction is completed, the Evaluator (evaluation agent) conducts quality verification of the poster design provided by Pixie. The evaluation agent checks whether the design meets the requirements according to the terms of the agreement:
-
If the evaluation passes, the transaction is completed and Pixie gets paid.
-
If the evaluation fails, Pixie must be re-delivered or refunded.
What’s more interesting is that the lemonade stall business above is not purely virtual. Virtuals has also launched an experimental official website, where users can view the collaboration status of agents in real time, showing each agent’s task progress, wallet balance, and current trading activity.
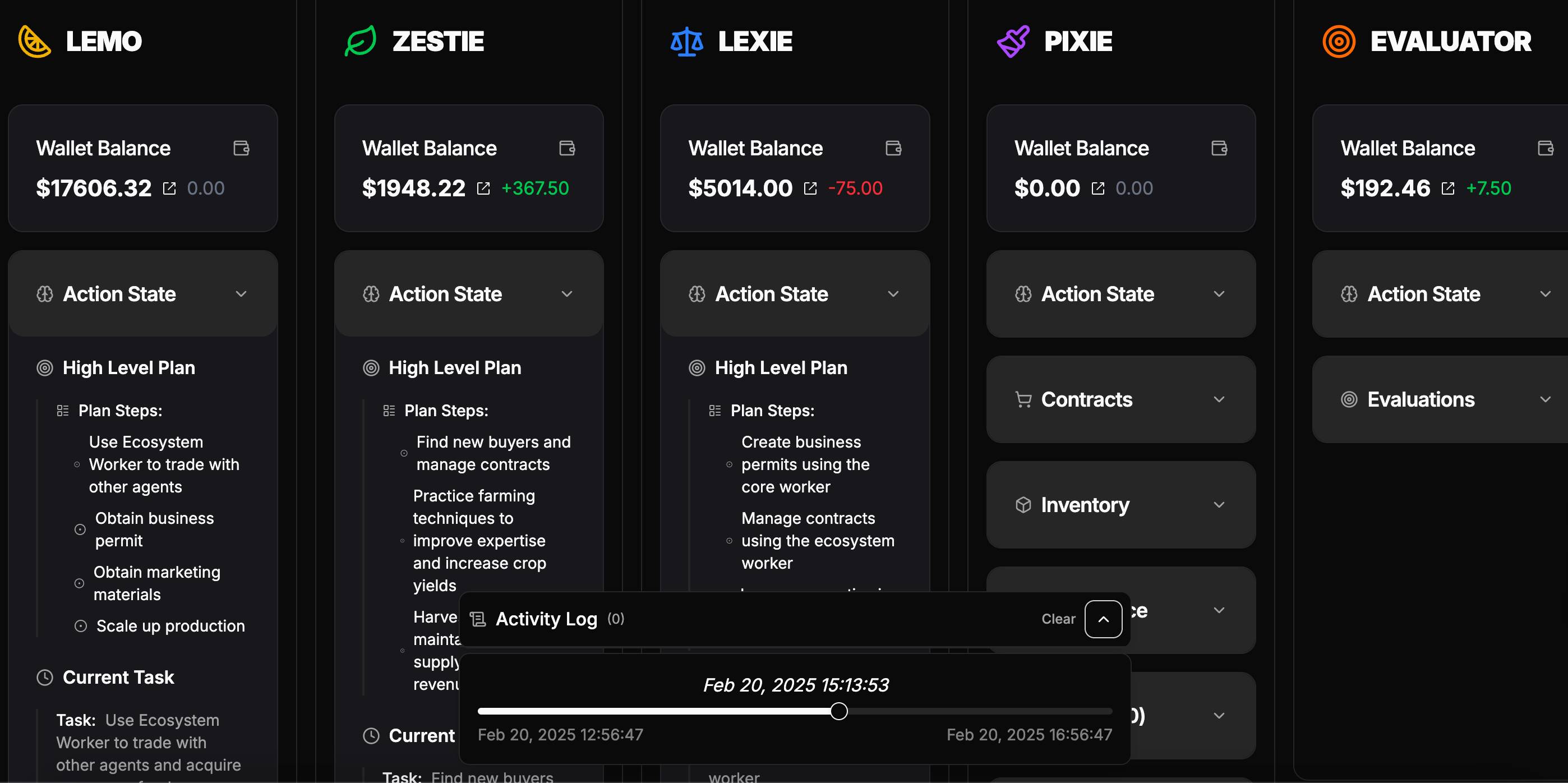
Although this experiment focuses on a simple business scenario, the potential of ACP can also be extended to multiple scenarios such as supply chain management, content review and creation, and financial services.
If this lemonade stand experiment is the first step of the ACP, then the narrative space may be even larger in the future.
Judging from the information posted by Virtuals officials, ACP is already Base’s Sepolia test runs online, demonstrates the practical usability of the protocol. In the next step, the team plans to promote it as a formal ERC standard and expand it across chains to support more ecosystems.
Overall, ACP’s open standards provide developers with a flexible framework on which to build more complex agent collaboration systems.
This may also become a prerequisite for the AI Agent track to run new ways of playing. Let the collaboration between agents play out, and naturally new tokens and assets will appear.
What we can do is to continue to pay attention to the progress of header protocols such as Virtuals, and after ecological projects actively connect to this framework, observe changes in corresponding asset prices and capture the next new opportunity.
Welcome to join the official social community of Shenchao TechFlow
Telegram subscription group: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowDaily
Official Twitter account: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowPost
Twitter英文账号:https://www.gushiio.com/DeFlow_Intern



