Analyze the core terms of the settlement agreement and their impact on industry compliance development.
Author: An Shouzheng Legal Service Co., Ltd.
On February 25, 2025, according to official OKX information, OKX’s Seychelles subsidiary reached a settlement with an investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice today, admitting that due to historical deficiencies in compliance controls, a small number of U.S. customers had traded on the company’s global platform.
According to the settlement agreement,OKX agreed to pay a 4 million fine and forgo approximately 1 million in revenue it earned from. customers during the period,Most of this comes from a small number of institutional clients. This article will provide a comprehensive interpretation of this incident, focusing on the core terms of the settlement agreement and its impact on the development of industry compliance.
1. The incident
timeline
Since 2018, OKX Seychelles has provided cryptocurrency spot and derivative trading services to U.S. customers through the global platform OKwww.gushiio.com. At that time, the cryptocurrency market was booming and new platforms were constantly emerging. Although OKX is headquartered in Seychelles, the U.S. Bank Secrecy Act and the Money Transfer Act stipulate that providing fiat exchange or asset transfer services to U.S. users requires a license from FinCEN and state regulators.
2018-2019 In 2008, OKX Seychelles did not fully assess the complexity of U.S. financial supervision and rushed to carry out business with the United States. At that time, global supervision of the crypto industry was in a gray area, and companies generally did not pay attention to compliance. The same was true for OKX Seychelles.
2019-2023 The issue of 2000 highlighted that OKX Seychelles has not obtained any state remittance business license in the United States, such as New York State BitLicense, Florida State Money Services License, etc. It used technical loopholes, such as insufficient IP address blocking, to allow about 32,000 U.S. users to conduct transactions, involving US$4.21 billion, accounting for 5% of global revenue. The scale of illegal business is large.
Specific manifestations of violations
1. Missing license plates and regulatory violations:Failure to apply for the MSB license of FinCEN in the United States makes it unable to meet the mandatory requirements of anti-money laundering (AML) and customer identity verification (KYC), and lacks the qualification to legally operate monetary services business.
Failure to obtain a state remittance license (such as California) violates state regulatory regulations on fund security, financial strength and risk management, and doubts about the legitimacy of the business.
2. The anti-money laundering mechanism fails:Enhanced due diligence (EDD) has not been carried out for high-risk U.S. customers (such as funds involving sensitive regions/industries), and the source path of funds and transaction purposes have not been traced, providing loopholes for illegal funds to launder. Violations of the core principles of the Bank Secrecy Act may become a channel for the circulation of transnational criminal funds.
3. Technical flaws in geo-fencing:Technical loopholes prevent the inability to effectively block U.S. IP access. Reasons include delayed IP database updates, algorithm loopholes, etc., allowing U.S. users to still use services in violation of regulations. A direct violation of Section 5330 of the Bank Secrecy Act and 18 U.S. Code Section 1960 (the crime of operating a remittance business without a license) constitutes a systematic compliance failure.
Investigation and reconciliation process
In 2022, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) jointly launched an investigation into OKX Seychelles, with the three parties working together:
DOJ: Verification of legal loopholes and business process compliance;DHS: Tracking the flow of funds and user information;CFTC: Special review of cryptocurrency futures trading violations.
Core terms of the settlement agreement (December 2023)
1. Economic penalties:OKX Seychelles was ordered to pay a fine of $84 million, of which $60 million went to the Justice Department and $24 million went to the CFTC.
2. Business Restrictions:OKX Seychelles not only has to give up $4.21 billion in U.S. customer revenue, but is also required to permanently withdraw from the U.S. market. This move completely cut off OKX Seychelles ‘business ties with the U.S. market and fundamentally eliminated the possibility of it continuing to operate illegally in the United States. The decision to permanently withdraw from the U.S. market has had a significant impact on OKX Seychelles ‘global business layout.
3. Compliance rectification:OKX is subject to review by an independent compliance monitor within the next three years. The independent compliance supervisor will comprehensively supervise all aspects of its business operations, including the implementation of anti-money laundering measures, customer identification processes, and transaction record retention. By introducing supervision from independent third parties, we ensure that OKX Seychelles truly establishes an effective compliance system and realizes the transformation from illegal operations to compliant operations.
2. Legal analysis
The core logic of U.S. encryption regulation
The United States ‘supervision of the encryption industry focuses on functional supervision. This regulatory concept is highly targeted and scientific.
1. Securities Law (SEC-led):Tokens are considered securities if they meet the Howey test. The Howey test mainly judges from four aspects: first, there is financial investment; second, investment in a common cause; third, it is based on reasonable expectations of future profits; and fourth, profits mainly come from the efforts of others.
For example, in some initial coin offering (ICO) projects, if investors purchase a token in the expectation of obtaining future benefits through the operations of the project team, and the value of the token mainly depends on the efforts of the project team, then the token is likely to be recognized as a security. Once identified as securities, the project party must comply with relevant provisions of the Securities Law, such as registering securities and disclosing relevant information.
2. Commodity Law (governed by CFTC):Bitcoin and Ethereum are classified as commodities. The CFTC regulates commodity futures trading in order to maintain fairness, fairness and transparency in the market. For futures trading of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, the CFTC requires trading platforms to have a complete risk management mechanism to prevent market manipulation and fraud. For example, the CFTC will strictly supervise the position limits of trading platforms and the reporting system for large accounts to ensure the stable operation of the market.
3. Anti-Money Laundering Law (FinCEN Enforcement):All entities involved in fiat currency conversion need to register MSB. This regulation is to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing from the source. Entities registered with the MSB must establish strict anti-money laundering procedures, including customer identification, transaction monitoring, suspicious transaction reporting, etc.
For example, when a cryptocurrency trading platform conducts fiat currency conversion business, it must authenticate each customer, verify the authenticity of their identity information, and monitor the customer’s transaction behavior in real time. Once a suspicious transaction is discovered, it must be promptly reported to FinCEN.
In this OKX case, the Ministry of Justice accused OKX of unlicensed remittance business rather than securities fraud, showing that it prefers to use mature financial regulations to crack down on cross-border violations. This is because OKX Seychelles ‘main violation is to conduct remittance business without permission, which directly violates the provisions of U.S. financial regulations on remittance business licensing. Compared with securities fraud allegations, accusations of unlicensed remittance business are more direct and clear, allowing for rapid and effective characterization and handling of violations.
Comparison of similar cases
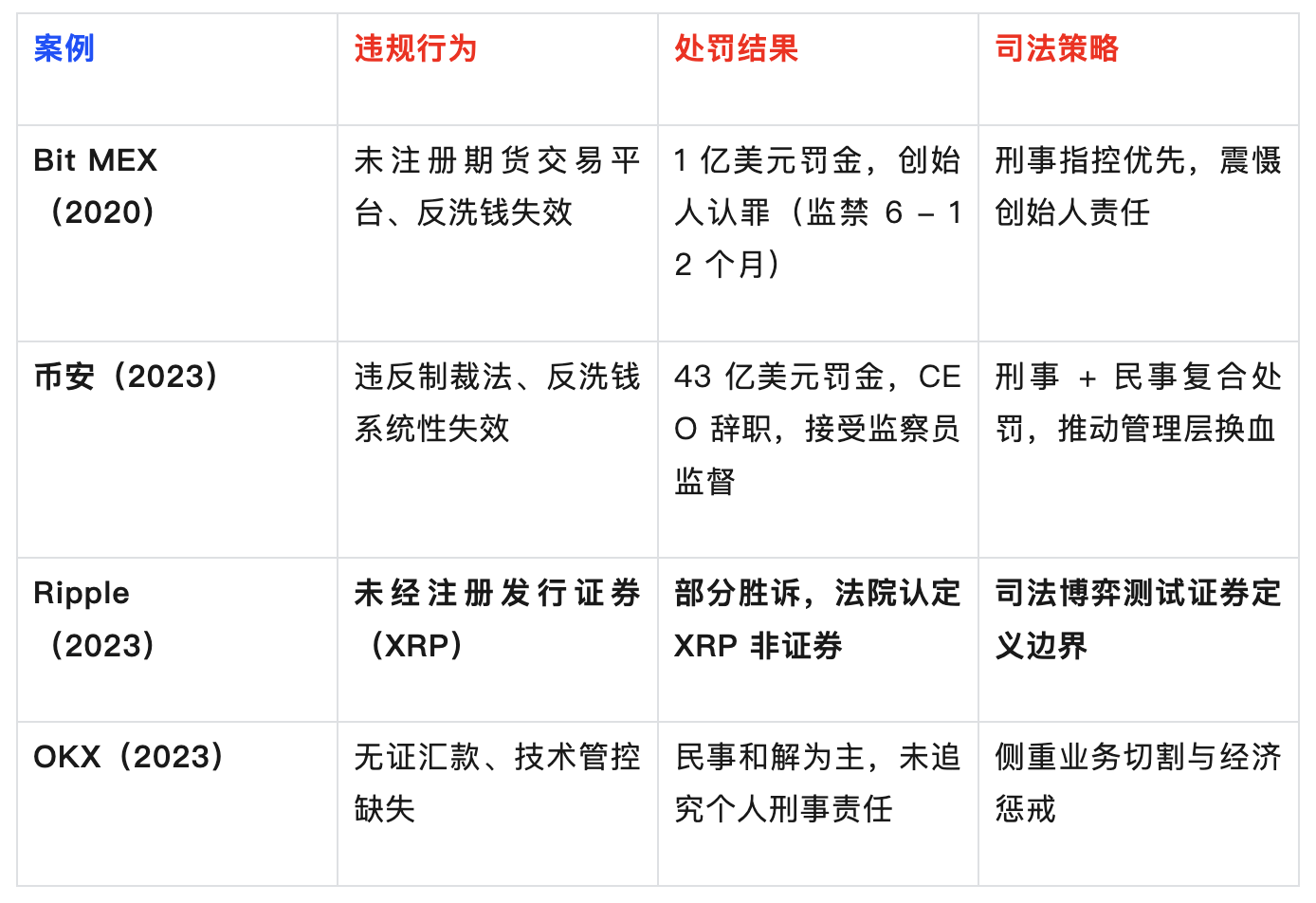
1. Sentencing gradient:Judging from the results of the punishment, Binance imposed the most severe punishment, with a fine of up to US$4.3 billion and the resignation of the CEO and acceptance of the supervision of the ombudsman. This is because Binance’s violations involved violations of sanctions laws and broke the red line of international sanctions.
BitMEX was fined US$100 million and its founder faced imprisonment. Its violations included unregistered futures trading platforms and ineffective anti-money laundering, which had a major impact on the compliance and stability of financial markets. OKX’s penalties were relatively light, mainly civil settlements, paying a fine of US$84 million, mainly because its violations were relatively concentrated in undocumented remittances and lack of technical control.
2. Judicial innovation:For the first time, the OKX case clearly listed technical flaws in geographical shielding as illegal requirements, providing a precedent for subsequent cross-border supervision. In previous cryptocurrency supervision cases, although attention was also paid to the application of technical means in compliance, technical flaws in geographical blocking were not separately listed as illegal requirements.
This judgment in the OKX case provides regulatory agencies with a clearer legal basis and regulatory direction when subsequently handling similar cross-border business violations, and further improves the regulatory framework of the cryptocurrency industry.
Legal significance of the settlement agreement
1. Efficiency priority:By settling, a lengthy litigation process is avoided. Take the Ripple case as an example, which lasted for three years, consuming a large amount of judicial and corporate resources. In the OKX case, fines were quickly recovered through settlement, and an agreement was reached only after more than a year of investigation, eliminating market violators, greatly improving regulatory efficiency, and allowing regulators to devote more energy to other important regulatory matters.
2. Balance of deterrence:The high fines paid by OKX (accounting for 20% of annual revenue) are enough to serve as a warning to the entire crypto industry and make other companies deeply aware of the serious economic consequences of illegal operations. However, no criminal charges were triggered, which preserved the company’s living space and gave the company the opportunity to rectify and re-operate in compliance. While deterring violations, this kind of punishment method also takes into account the development needs of the industry to avoid excessive severe penalties leading to the closure of enterprises and causing unnecessary impact on the industry.
3. Compliance guidance:Mandatory the introduction of independent supervisors and promote enterprises to establish verifiable compliance systems. The existence of independent supervisors makes OKX must accept the supervision and guidance of external professional organizations in the process of establishing a compliance system to ensure that its compliance measures are truly and effectively implemented. This not only helps OKX itself achieve compliance operations, but also establishes a compliance construction model that can be used for the entire encryption industry and promotes the improvement of the overall compliance level of the industry.
3. Research and judgment on global regulatory trends
Global crypto asset regulation has shown a multi-dimensional strengthening trend in recent years. The European Union’s Crypto Asset Markets Act (MiCA) will come into effect in 2024, requiring exchanges to provide white paper filings and reserve certificates; the United States has established a Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team (NCET) to strengthen cross-departmental law enforcement collaboration;FATF travel rules have been extended to DeFi, requiring DApp developers to attach user information to on-chain transactions; at the same time, the United Arab Emirates and Singapore have used loose licenses to attract compliant companies, forming regulatory competition with Europe and the United States.
The OKX settlement highlights the need for crypto companies to internalize compliance into core competitiveness under the US-led regulatory framework. Compared with Binance’s strategy of expanding first and then rectifying, Coinbase invested heavily in compliance in the early stage, achieved high global license coverage and became the preferred partner for traditional institutions.In the future, only companies that integrate compliance into their technical architecture, organizational culture and business strategy will be able to seize the lead in regulatory reshuffle.
Welcome to join the official social community of Shenchao TechFlow
Telegram subscription group: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowDaily
Official Twitter account: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowPost
Twitter英文账号:https://www.gushiio.com/DeFlow_Intern



