Wen| Xiaguangshe, author| Liu Jingfeng
At the beginning of 2025, the world’s painting styles have gathered on AI.
After China’s DeepSeek stunned the global science and technology community, it seemed that the whole world was developing large models and building data centers in an instant.
Musk said that xAI will also release its own model soon, even better than DeepSeek; French AI star startup Mistral AI recently released Le Cha, the world’s fastest “AI super assistant” for the first time, 13 times faster than ChatGPT; The Indian government has also announced that it will develop a local large-language model in the next 10 months to challenge DeepSeek and OpenAI.
“StargatePlan: Invest US$500 billion in the next four years to build as many as 20 ultra-large data centers.
Meanwhile, in January this year, British Prime Minister Keir Starmer also announced an ambitious action plan for artificial intelligence opportunities,Make Britain“AISuperpowers.To this end, technology companies have committed £ 14 billion to create 13250 new jobs, including major data center projects in Wales and Liverpool.
Britain’s neighbor, France, just hosted a two-day artificial intelligence action summit yesterday. On the eve of the summit, French President Macron announced that France would invest more than 109 billion euros (about 113 billion US dollars),Create a French version of the Stargate”。Now, 35 locations have been identified in France for the construction of data centers. Macron hopes to build Europe into a leader in the field of artificial intelligence (AI).
India is also investing heavily in AI. In January this year, Reliance Group, led by India’s richest man, Mukesh Ambani, announced that it would build a global network in Jamnagar, India.The world’s largest super data center with capacity, the total investment is about 20 – 30 billion US dollars.
During the LEAP exhibition being held in Saudi Arabia this year, Datavolt signed a US$5 billion agreement with Neom to planBuild one of the world’s largest artificial intelligence data centers。The construction of artificial intelligence in Middle Eastern countries is also on the fast track.
Will 2025 really be the year when AI changes the world?

DeepSeek’s explosion came suddenly. On the morning of January 27, DeepSeek hit the top spot in downloads on the Apple App Store free lists in both China and the United States, surpassing ChatGPT, which originally dominated the list. Half a month ago, DeepSeek’s App was just launched in the iOS and Android application markets.
This is the first time an application from China has achieved this achievement. Moreover, it scared everyone at once.
Because DeepSeek-R1 ‘s model is tied to OpenAI o1 in all capabilities, the total training cost is only US$5.576 million; while the training cost of the GPT-4o model is about US$100 million.
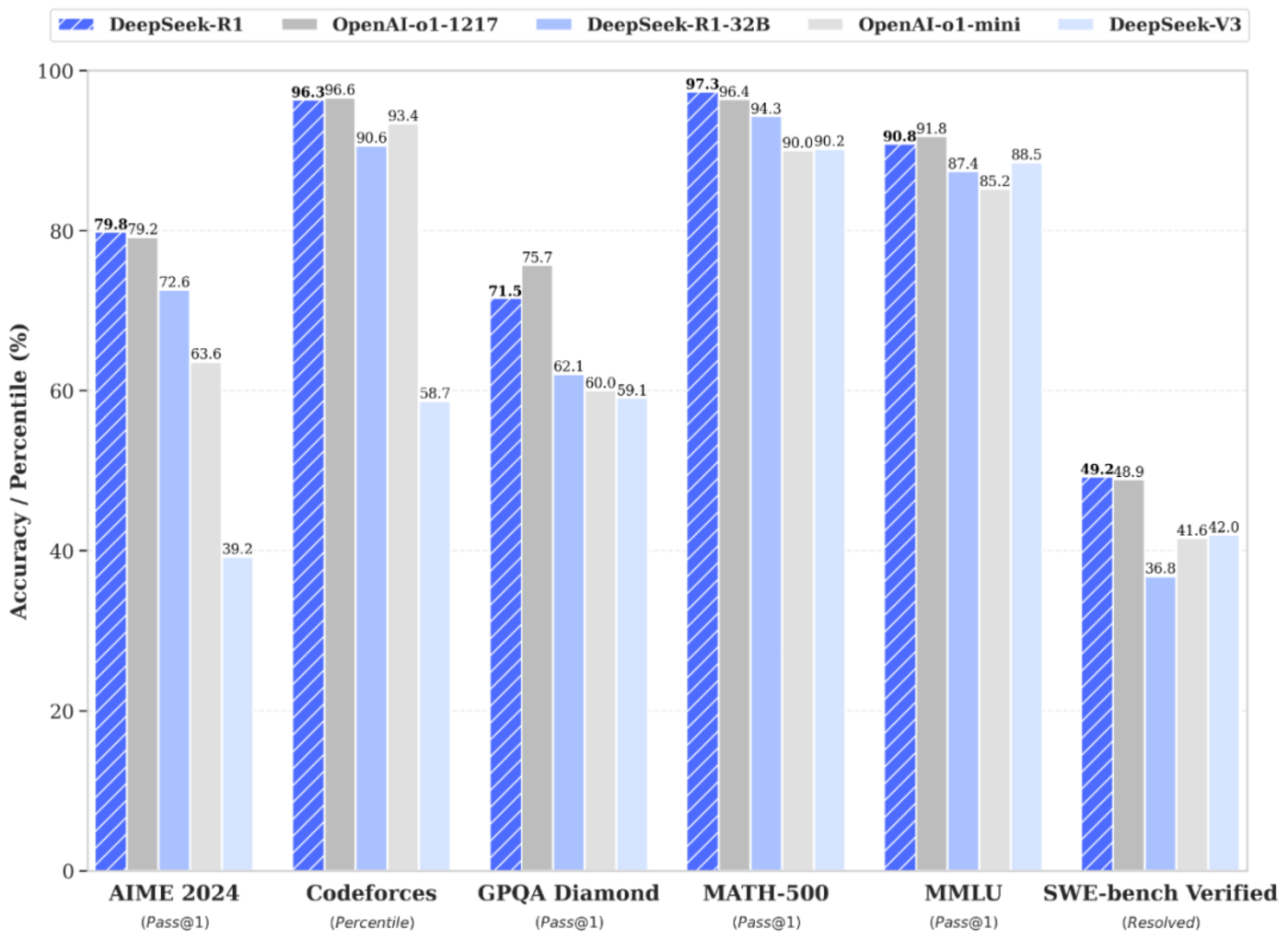
As a result, the world began to truly realize that China’s explosive potential in the field of AI models, even with extremely limited resources, China can create its own big model by adjusting the big model infrastructure.
Subsequently, many countries showed panic: Australia Treasury Secretary Jim Chalmers called on citizens to be cautious when using DeepSeek, and banned the use of China’s artificial intelligence DeepSeek on government systems and devices; South Korea has strengthened supervision of DeepSeek related applications, and relevant departments have begun to review companies that use DeepSeek; France and Ireland have questioned DeepSeek on the grounds of data security; Italy directly announced the ban of DeepSeek; and the U.S. Congress has introduced a new bill that downloading DeepSeek can be sentenced to up to 20 years in prison.
In addition to panic, there was more awakening.
To this day, ChatGPT is still the weathervane of global models, but after the popularity of DeepSeek, it also had to change. On January 24, OpenAI will directly free the ChatGPT O3Mini version, which originally cost a subscription price of US$200 per month. And on February 1, OpenAI also launched its latest reasoning model o3-mini. Similar to DeepSeek, o3-mini also adds online search and display of thought processes. Moreover, in terms of usage rights, ChatGPT has also opened the o3-mini model to all users for free. ChatGPT Pro users can enjoy unlimited access, while the message limit for Plus and Team users has increased from 50 to 150 per day.
Musk recently said after experiencing DeepSeek that you can expect that China will do many great things, and DeepSeek is one of them. But what he seems to want to make most of all is thatFounded by himxAIIt is also about to release its own model, even better than DeepSeek. The new model is called Grok-3, and its pre-training is said to have been completed, usingcomputing powerTen times more than Grok-2。Greg Yang, a mathematician at xAI, also demonstrated his dialogue with Grok-3 on the platform on January 19 this year. There are signs that Musk is actively joining this big model battle.
On February 6 this year, French AI star startup Mistral AI also released the iOS and Android apps of Le Chat, the world’s fastest “AI super assistant”. It has real-time access to the Internet and multimodal capabilities. It is not only free, but it is said to have feedback speeds 13 times faster than ChatGPT. In just a few days, Mistral climbed to the top of the French App Store. French President Macron has also mentioned the name of the app, Le Chat, many times in a program recently, incarnate as a salesman and also called on French people to download it.
Affected by the current AI boom, on January 30 this year, the Indian government stated that it plans to develop a local large language model in the next 10 months to challenge DeepSeek and OpenAI. Indian Information Technology Minister Vishna said that with the basic work completed, the Indian government is currently focusing on building an artificial intelligence system that meets India’s unique needs. It is expected that by the end of this year, six major developers will launch basic AI models. According to Indian media, the Indian government has approved 18 proposals aimed at accelerating the implementation of AI solutions in key areas such as agriculture and climate change. These support measures include providing computing power, data and funding.
Earlier, on December 17, 2024, the United Arab Emirates government-backed Technological Innovation Institute (TII) announced the launch of Falcon 3, the institute’s latest generation of open source small language models (SLM). Compared with Large Language Models (LLMs), SLM has fewer parameters, simpler design, and has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, and ability to be deployed on resource-limited devices. That is, it can run efficiently on lightweight infrastructure such as laptops.
Of course, before this, the United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, Russia, Canada, and Israel also had their own big models. Today, this competition has reached a new climax.
Muath Alduhishy, executive officer of Advanced Research, Development and Innovation (RDI) at Saudi Information Technology Corporation (SITE), used sovereign AI to summarize this trend. This shows that current AI has actually exceeded the scope of technology and business and become a kind of Sovereign AI.

What is the current global AI situation for countries?
As the most influential institution in the world’s AI field, Stanford University released the “Global Artificial Intelligence Strength Rankings” on November 21, 2024. Through 42 indicators, it comprehensively evaluated and ranked the artificial intelligence activity of 36 countries.
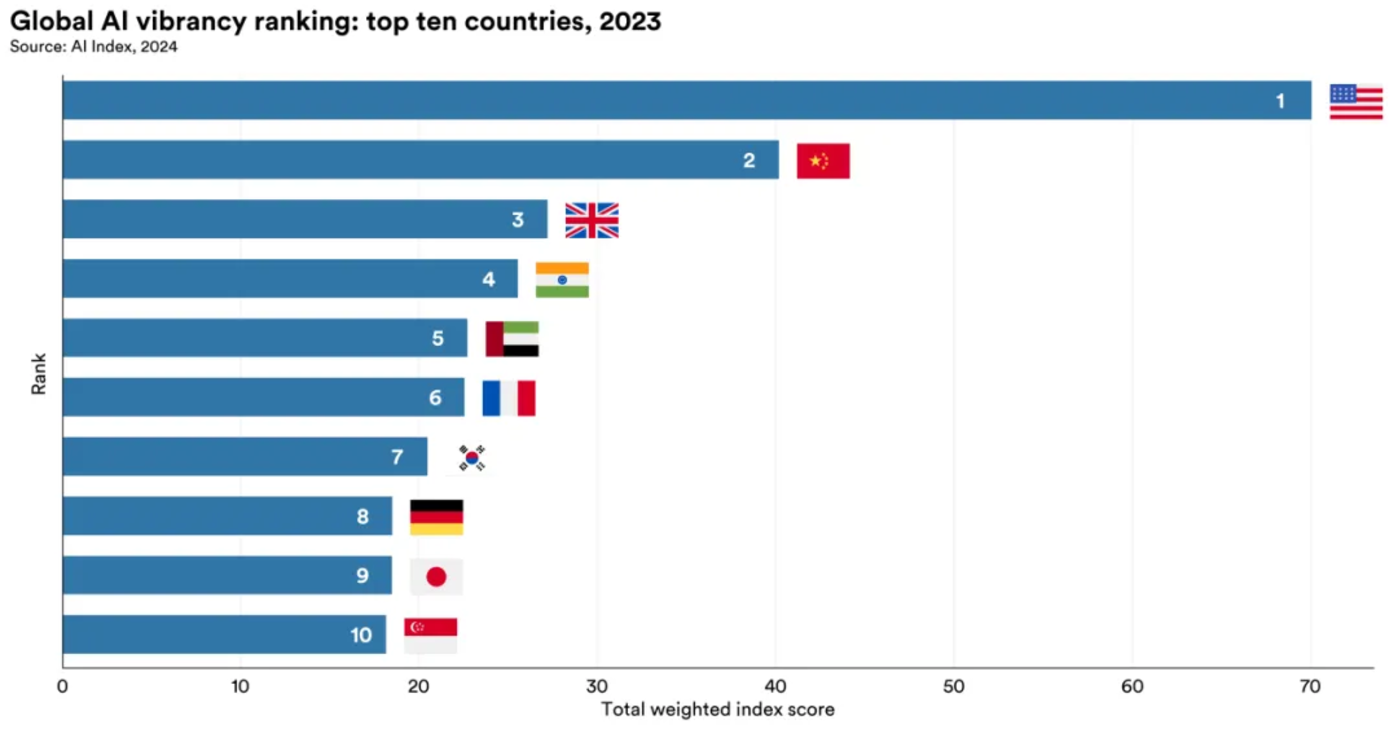
Global artificial intelligence vitality ranking: top ten countries in 2023
Among them, the United States ranks first in the total weighted index. In terms of developing famous machine learning models, the United States will reach 61 models in 2023. Among them, the most representative ones are ChatGPT owned by OpenAI, Gemini owned by Google, etc. In addition, the United States has adopted a positive attitude towards artificial intelligence regulation, passing a total of 23 artificial intelligence-related laws since 2017.
China ranks second. China performs well in R & D, economy and infrastructure. Thanks to the huge market, sufficient infrastructure such as network and computing power, and the data support provided by large-scale industrial production capacity, many excellent large models have emerged in China, including large models from major manufacturers such as Baidu, Ali, Tencent, Byte, Huawei, and iFlytek, as well as models developed by startups such as DeepSeek, Kimi, and MiniMax.
In addition, the report also stated thatChina isAIInnovation has shown strong growth momentum, especially in patent applications, where the number of AI patents granted is almost three times that of the United States. This is also China’s AIlarge modelAn important support that can quickly go from following to breaking through originality。
The UK ranks third, with outstanding performance in R & D, education, policy and governance. India ranks fourth and United Arab Emirates ranks fifth. France ranks sixth and performs strongly in policy and governance, education, and infrastructure. South Korea ranks seventh. In October 2023, South Korean telecommunications company KT released the country’s first AI model Mi: dm. However, South Korea’s AI model is mainly dominated by large chaebol companies and lacks an active start-up ecosystem. Germany ranks eighth, is an important contributor to AI research and ranks fourth in producing famous machine learning models. South Korea ranks among the top ten, along with Japan and Singapore, highlighting the growing importance of AI in Asian economies.
Stanford University said that in this ranking, the performance of different regions highlights the global nature of AI and the different strategies adopted by countries to promote development and deployment in this field.Many national leaders have realized the geopolitical significance of AI and are working hard to improve the level of AI development in their countries.
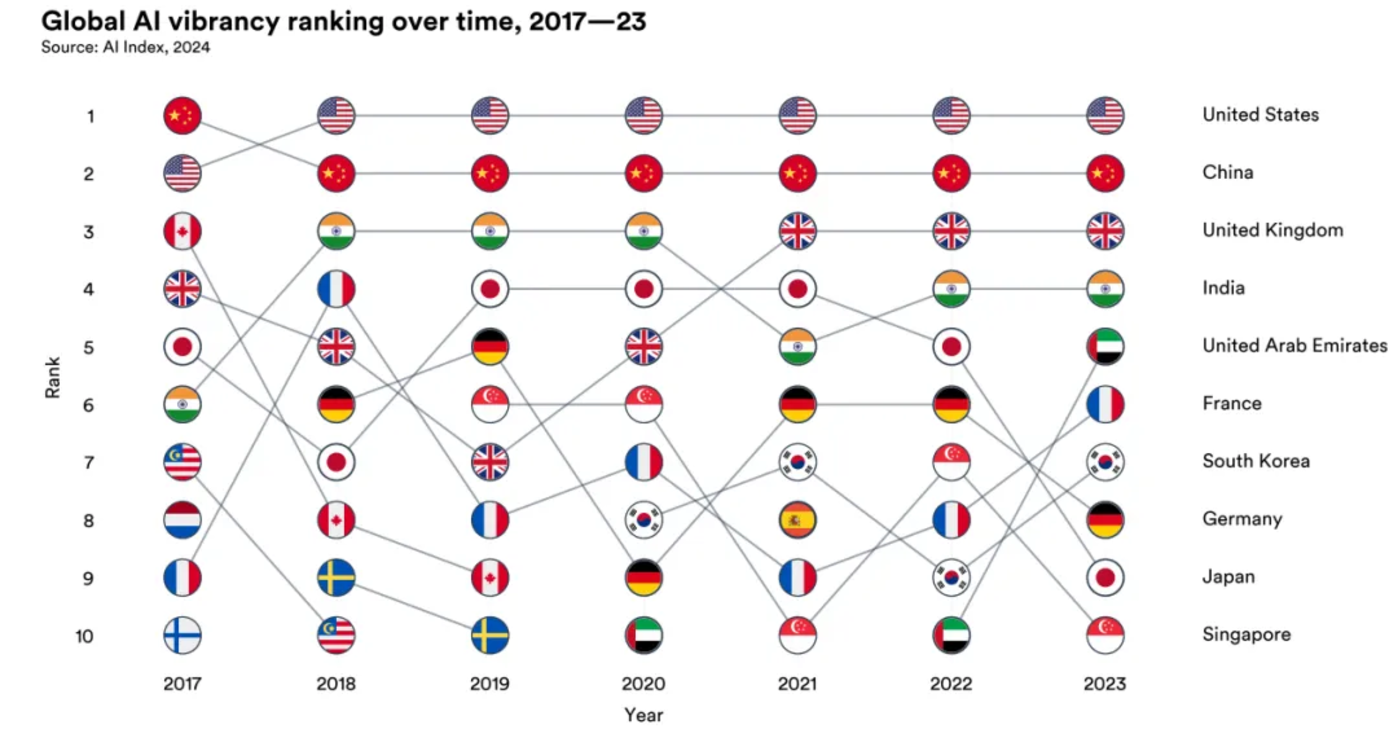
Global artificial intelligence vitality changing competitive trend from 2017 to 2023
The above figure shows the changing competitive trend of global AI vitality from 2017 to 2023. It reveals three different levels of competition: the first level is always dominated by the United States and China; the second level is relatively stable, including the United Kingdom and India; and the third level is greatly changed, with countries such as France, Germany, Japan, Singapore and South Korea often swapping positions in this level.
There is no doubt that the United States and China have become the focus of global AI competition, and the gap between latecomers continues to widen.

From February 10 to 11, the Global Artificial Intelligence Action Summit was held in Paris, the capital of France. The summit was attended by representatives from about 100 countries, including heads of state, business leaders, scientists and members of civil society, to discuss the application of artificial intelligence and global governance issues.
At the conference, French President Macron announced that France will invest nearly 109 billion euros in the development of artificial intelligence to create a French version of Stargate. Among them, on February 6, France and the United Arab Emirates jointly announced a strategic framework agreement to build a 1 GW AI data center in France, with an investment scale expected to reach US$30 billion to US$50 billion. In addition, Canadian investment giant Brookfield Asset Management also plans to invest 20 billion euros in French AI infrastructure by 2030 to help Europe catch up with China and the United States in the AI field.
Macron believes that if France and Europe do not want to be eliminated in the development of global AI, they need to accelerate their catch up. He hopes that Europe will become a leader in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), and the first battle will be investment, investment, investment. Currently, 35 locations have been identified in France for the construction of data centers. According to the France 2030 plan, the French government will invest an additional 400 million euros to support nine artificial intelligence clusters, including Rennes, Saclay, Grenoble, Toulouse, etc. These clusters will undertake interdisciplinary research and provide additional training.
“The Stargate is a plan proposed by U.S. President Trump after taking office in January this year. It is called the largest artificial intelligence infrastructure project in history.
The plan is to establish a joint venture called Stargate between OpenAI, SoftBank of Japan and Oracle of the United States to invest US$500 billion in AI infrastructure in the United States within four years.
In fact, since the explosion of ChatGPT, the demand for high-performance computing and storage has continued to increase, and the construction of data centers in the United States has continued to be booming, even becoming the hottest commercial real estate in the United States. Technology giants such as Google, Microsoft, and Meta have entered the company and invested billions of dollars in data center expansion.
China proposed new infrastructure plans including data centers as early as 2020. Since then, Alibaba Cloud announced that it will invest 200 billion yuan in three years to build a data center, Tencent will invest 500 billion yuan in five years to deploy new infrastructure, and Baidu will increase the number of intelligent Cloud Virtual Machine servers to 5 million units within 10 years.
In order to coordinate the layout of energy, data and other resources, the country has also proposed the Eastern Data and Western Computing Project. Using the Eastern Data and combining the energy advantages of the western region, it has laid out a big chess game for the transformation of the data center industry.
As another organizer of the Paris AI Action Summit, India has also recently made great strides in data center construction.
On January 31, India’s Reliance Group announced plans to invest US$20 billion to 30 billion to build a data center with an installed capacity of 3GW in Jamnagar, India. If the project is implemented as planned, it will become the largest data center in the world.
This ambitious data center plan has attracted the attention of many international investors, including technology giants such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, who have increased their investment in data centers in India. For example, Microsoft announced in early January this year that it would invest US$3 billion in India over the next two years to build new data centers and promote the development of AI technology; while Amazon Cloud Technology announced on January 23 that it would invest US$8.3 billion in Maharashtra’s cloud infrastructure as part of a plan to invest US$12.7 billion in India by 2030.
In the past, India fell relatively behind in terms of the number of ultra-large data centers. As of 2023, India has only about 18 ultra-large data centers, while China has nearly 100. But in the coming years, India’s data center market is expected to grow significantly. According to India’s Ministry of Electronic Information Technology, India’s data center capacity is expected to increase from the current 819 megawatts (MW) to 1800MW by 2026.
Nowadays, as the competition for large models kicks off, the arms race for global data centers has begun to reach a climax.
At the same time as the Paris AI Summit, the fourth LEAP exhibition is also being held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. At this year’s LEAP exhibition, artificial intelligence and digital economy also became the hottest topics. At the meeting, Cliff Chau, managing partner of Ida Capital, joined hands with Hazman Hilmi Sallahuddin, chief investment officer of the Malaysian Civil Servants Pension Fund (KWAP) and other guests to discuss “Cross-border Investment in Asia and the Middle East: Collaboration on Technology and Digital Infrastructure”. In fact, Saudi Cloud Computing Corporation (SCCC), Saudi Arabia’s leading cloud service provider, was established by a joint venture between Eda Capital, Saudi Telecom and Alibaba Cloud.
During the LEAP exhibition, several global technology giants announced new plans in Saudi Arabia: Tencent Cloud announced that it will invest more than US$150 million in the Middle East in the future (approximately 1.096 billion yuan), used for infrastructure, resources and related investment, and to build the first Middle East data center in Saudi Arabia; American data center giant Equinix announced an investment of US$1 billion to build a 100MW AI data center; Datavolt signed a US$5 billion agreement with New Future City to plan to build one of the world’s largest AI data centers.
During this period, Lenovo also held a groundbreaking ceremony for its new manufacturing base in Riyadh. The factory has an annual output of one million computers and servers and will be officially put into operation in 2026.
Also on February 11, the 2025 World Government Summit kicked off in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Artificial intelligence and digital economy have become one of the core topics of the summit. At the meeting, Baidu founder Robin Li had a high-profile dialogue with United Arab Emirates AI Minister Omar Sultan Oama. He pointed out that continuous investment in chips, data centers and cloud infrastructure is still needed to create better and smarter next-generation models. Orama said he hopes that at next year’s conference, all teams will be autonomous driving supported by Radish Run. rdquo;
Recently, the United Arab Emirates has also been intensively deploying data center construction. In addition to the AI data center it has just announced with France, on February 5, the United Arab Emirates signed a cooperation agreement with the Colombia Agency, which will help Colombia establish three strategic data centers in its northern city of Santa Marta.
On January 13 this year, British Prime Minister Stammer announced the British government’s artificial intelligence action plan. The plan will make the UK a world leader in this field. The government has promised to increase the country’s computing power by 20 times by 2030 and build new supercomputers to meet the computing power needs of AI products.
Along with the announcement of this plan, a number of large technology companies have pledged to invest a total of 14 billion pounds (about 17.4 billion US dollars) in the UK to build the artificial intelligence infrastructure needed by the UK. For example, London-based AI infrastructure company Nscale announced plans to invest US$2.5 billion (£ 2 billion) in the UK data center industry over the next three years. In October last year, the four major U.S. technology companies, ServiceNow, CoreWeave, CyrusOne and CloudHQ, announced that they would jointly invest 6.3 billion pounds (about 8.2 billion US dollars) in data center construction in the UK.
In September 2024, Peter Kyle, the British Secretary of State for Science, Innovation and Technology, announced that the government had listed the UK’s data center as a critical national infrastructure. The UK ranks third in the world in terms of the number of data centers, with most data centers concentrated in London and along the M4 highway. But energy needs in these areas are huge, causing projects to be delayed or stopped due to insufficient power capacity.
The above-announced data center construction plans in several major countries around the world alone cost US$700 billion. This data center battle around the leadership role of AI can be described as extremely fierce.
Still, a huge test lies ahead.

Although the importance of data centers is self-evident, the more data centers the better and the bigger the better.
In essence, data centers sell electricity. Among the current data center operating costs, IT electricity bills account for more than 30%, and environmental electricity bills (cooling, lighting, etc.) account for about 20%. The combined proportion of the two exceeds 50%. Even in some old and small data centers, as the PUE (Power Efficiency) of the data center becomes higher, electricity bills will account for more than 60% of operating costs.
The upper limit of the supply of data center projects in a region depends on the supporting power facilities in the region, which is limited by power grid planning.
Take the United States as an example. Data centers in the United States are mainly located in northern Virginia. Currently, the state’s high-voltage transmission line capacity has reached its limit, putting new data center projects at risk of delays. In response to this problem, Virginia passed a bill to speed up the approval of $60 million in power transmission projects, a move supported by multiple industry giants including Amazon.
According to the Industrial Information Resources Corporation (IIR), it is expected that by 2030, U.S. data center power demand will more than double from 17GW in 2022 to 35GW.
In order to cope with growing power demand, data center operators are also constantly improving their technology. For example, using advanced cooling technology and renewable energy, data centers are gradually developing in a green and environmentally friendly direction. Many data centers are also using wind and solar energy to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources.
In addition, the rapid development of the data center industry has also triggered discussions on land resources and environmental protection. For example, Microsoft’s new project is expected to lose nearly 8 acres of wetlands and more than 1600 feet of streams and rivers, a situation that has attracted attention and discussion from environmental groups. In the future, how to meet the needs of data center construction while taking into account environmental protection will become an important issue in the development of the industry.
A few years ago, China’s data centers also encountered growth bottlenecks due to energy and environmental issues. However, since 2022, the country has coordinated resource planning and implemented the major project of Eastern Digital and Western Computing. The national integrated big data center system has completed the overall layout design, creatively combining Eastern Data with Western Energy, solving this problem.
However, in contrast to overseas countries, there are few action cases of overall planning of data centers. Especially in countries that cannot maintain a large and stable supply of electricity, blindly building data centers may encounter an energy crisis and affect the healthy development of the data center industry.
In addition, the most important value of data centers is to promote the development of the digital economy. However, the development of overseas digital economy does not occur overnight. Blindly deviating from the development level of the local digital economy and building a large data center, it is likely to encounter problems such as vacant data center computer rooms and insufficient shelves.
In fact, in recent years, domestic data center-related companies have been accelerating their journey to sea. Leading cloud service providers such as Tencent Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and Huawei Cloud have begun to deploy data centers in Southeast Asia, the Middle East and other markets several years ago; in addition, Qinhuai Data, Century Internet, Halo New Network, Wanguo Data and other third-party IDC service providers such as Runze Technology have also gone abroad to invest, build, and operate data centers overseas.
Compared with European and American data center giants, China’s IDC companies are rapidly deploying in emerging markets and deeply integrating into the construction of the local data economy to promote the development of the local digital economy.
It is foreseeable that in the global AI competition, China’s new infrastructure experience will highlight greater value.
References:
[1]Stanford University released: “Global Artificial Intelligence Strength Rankings”, Global Technology Map



