In January 2025, losses caused by vulnerabilities, hackers and fraud were approximately US$98 million, and 28 cryptocurrency hacking attacks occurred, of which approximately US$8 million was attributed to phishing.
Time to watch the monthly security incidents of zero-time technology begin! According to statistics from some blockchain security risk monitoring platforms, the losses caused by vulnerabilities, hackers and fraud in January 2025 were approximately98 millionDollar, incurred28 timesCryptocurrency hacking attacks, among which about800 millionDollar attributed to phishing. But compared with a loss of US$133 million in January 2024, the decline is lower.44.6%。This is down from the $23.58 million loss in December 202456%。
Hacking
Typical security incidents7 plays
(1)On January 8, more than $800,000 was stolen from users of Orange Finance (the DeFi protocol on Arbitrum). Attackers can access the protocol’s management keys and use these keys to perform malicious upgrades to the protocol’s contracts, thereby stealing the wallets of all users with valid token approvals for the protocol.
(2)On January 8, a private key breach occurred in Moby, affecting some LP assets in certain agreements. They said it was not a security issue related to protocol smart contracts, but that hackers were trying to steal funds by simply upgrading existing smart contracts using stolen proxy private keys. Finally, tonykebot took advantage of the lack of protection in the UUPS implementation to carry out a successful white hat rescue operation, returning 1.47 million USDCs obtained by hackers previously attacking the on-chain options protocol Moby.
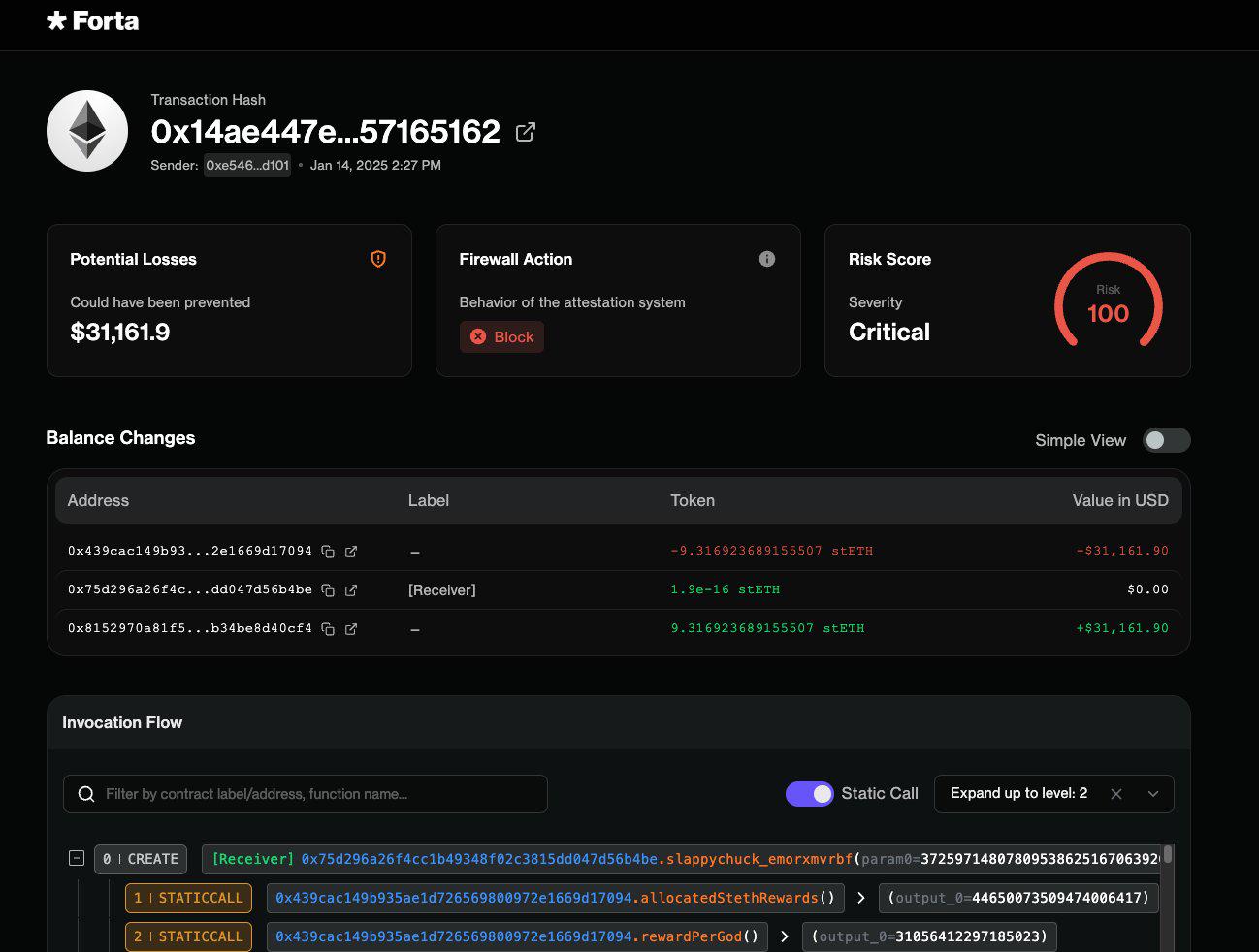
(3)On January 13, according to monitoring by the zero-time technology security team, UniLend on the EVM chain was attacked and lost approximately US$197,000. The cause of this vulnerability was that when Unilend was conducting a redeem, it did not subtract the amount of collateral that the redeem should transfer out when calculating the amount of collateral, resulting in an erroneous calculation that the amount of collateral was higher than the amount of collateral actually owned by the attacker, and the redemption should not have been successfully completed. Eventually, the attacker emptied the project party’s stETH tokens.
Detailed attack analysis can be found here:
Zero Time Technology|| Analysis of Unilend Attack Events
(4)On January 15, the zero-time technology project team monitored multiple attacks on the Ethereum chain project Sorra, which caused a total loss of 41,000 USD. The cause of this vulnerability is that the Sorra project did not determine whether the user had extracted reward when withdrawing, resulting in the user being able to repeatedly extract reward through a large number of operations. The attacker used the above vulnerability to initiate multiple transactions and extract all SOR Tokens in the Sorra project.
Detailed attack analysis can be found here:
Zero Time Technology|| Analysis of SorraStaking Attack Event
(5)On January 21, Forta detected a $324,000 vulnerability on TheIdolsNFT.
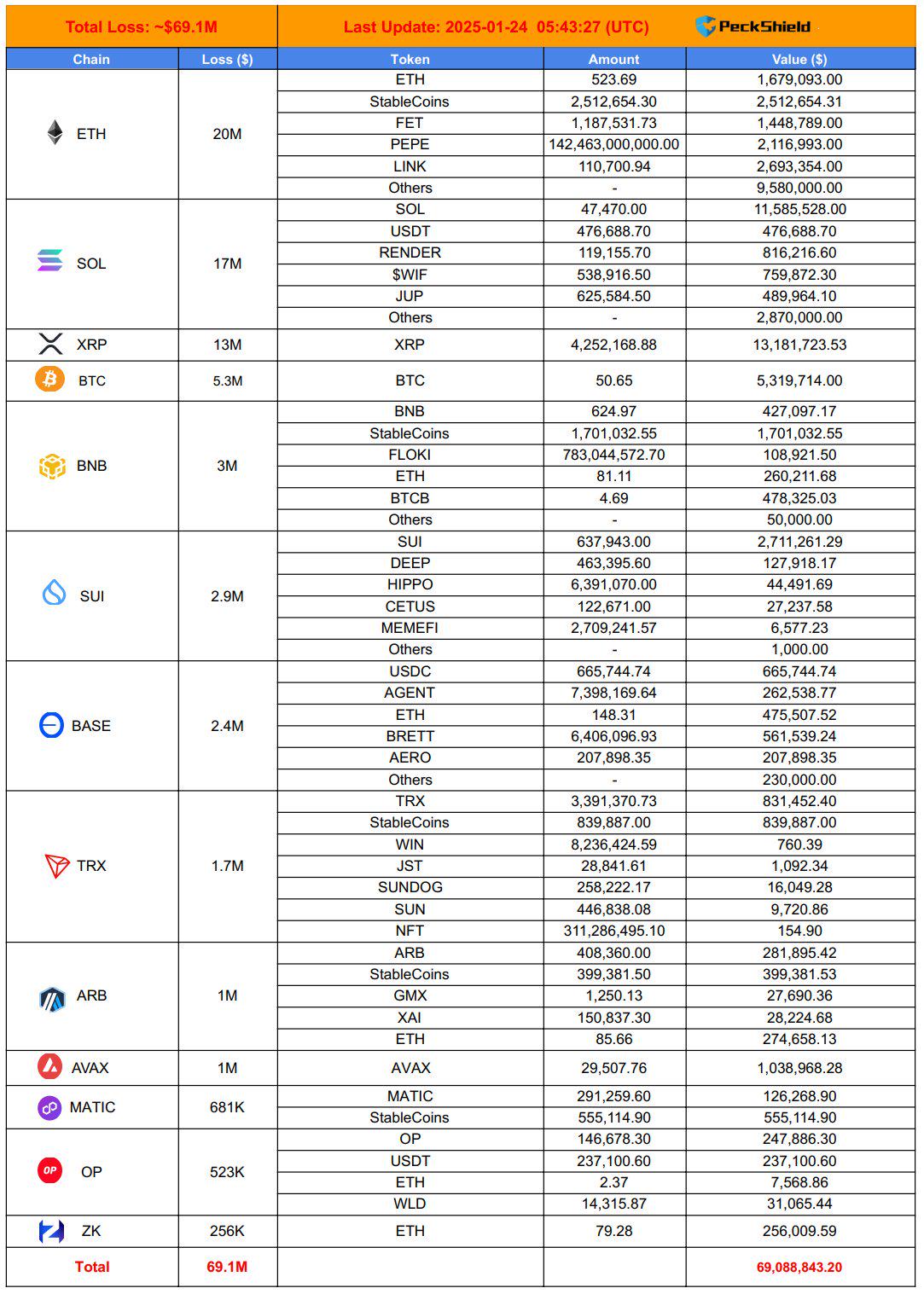
(6)On January 23, the hot wallet of the Singapore-based Phemex cryptocurrency exchange was attacked, resulting in losses of approximately US$70 million.
(7)On January 24, according to monitoring by the Slow Fog Security Team, due to the lack of input verification in ODOS, the vulnerability had been exploited on multiple chains, resulting in a loss of approximately US$100,000. ODOS tweeted that the attack exploited a vulnerability in its audited executor contract to steal revenue stored in the contract, but did not affect any user funds.
Rug Pull /Phishing Fraud
Typical security incidents10plays
(1)On January 2, a $VIRTUAL holder holding approximately 39 times ($196,396) in tokens lost all of his tokens due to an “increased limit” phishing transaction.
(2)On January 3, a $RLB holder lost all tokens worth approximately $1 million due to an “Uniswap Permit2” phishing signature.
(3)On January 6, the address starting with 0x5167 lost $155,256 worth of EIGEN after signing an “increased subsidy” phishing transaction.
(4)On January 7, an address starting with 0x8536 lost US$103,020 worth of tokens after signing the “Uniswap Permit2” phishing transaction.
(5)On January 8, the address starting with 0x3402 lost $474,422 worth of $OLAS,$SEKOIA,$VIRTUAL and $FJO after signing multiple phishing signatures.
(6)On January 14, an address starting with 0x00c0 lost $263,255 worth of $VIRTUAL after signing a phishing transaction.
(7)On January 17, an address starting with 0x80dc lost USUALUSDC+ worth US$426,106 after signing a “license” phishing signature.
(8)On January 20, an address starting with 0x1e70 lost $135,068 worth of WETH after signing a “allow” phishing signature.
(9)On January 22, the address starting with 0x3149 lost $553,045 worth of $PAXG after signing a “transfer” phishing transaction.
(10)On January 29, the 0xeb2 starting address lost $384,645 worth of $LINK after signing an “increaseApproval” phishing transaction.
summary
Cryptocurrency phishing scams stole $10.25 million from 9,220 victims in January, down 56% from a loss of $23.58 million in December. However, criminals are constantly evolving and adopting more complex attack methods.
The zero-time technology security team recommends that the project party always remain vigilant and remind users to beware of phishing attacks. Users are recommended to fully understand the project background and team before participating in the project, and carefully choose investment projects. In addition, internal security training and authority management need to be done well, and a professional security company must be found to conduct audits and conduct project background investigations before the project goes online.



