Wen| Wang Jiwei
Almost every Spring Festival, some major events occur in the scientific and technological world, especially in the AI field that has been changing rapidly in recent years.
In previous years, foreign products attracted attention, but this year, China’s technology stunned the world.
DeepSeek-R1, a large model quantitatively released by Magic Square before the Spring Festival, quickly exploded in the AI field as soon as it was unveiled. Business managers, entrepreneurs, project managers, analysts and even relevant department leaders around the world have spoken out and lamented DeepSeek-R1 ‘s breakthrough in the field of large models.
DeepSeek-R1 uses large-scale reinforcement learning technology in the post-training stage, which enables significant improvement in reasoning capabilities even with very little annotated data. Advances in this technology have enabled it to demonstrate performance comparable to the latest version of OpenAI in multiple tasks such as mathematics, code and natural language reasoning, truly achieving open source. This means that the AI field is moving towards low cost + high performance.
What is important is that many agent practice cases such as browser-use based on DeepSeek-R1 have proved that DeepSeek can effectively reduce the threshold for deploying AI Agents, greatly improve the performance and efficiency of AI Agents, and enhance scenario adaptability.
At a time when LLM Based AI Agents are in urgent need of implementation, the importance of an efficient and cost-effective large model to agents can be imagined. It is foreseeable that the next reinforcement learning models such as DeepSeek-R1 will greatly improve the efficiency of agent construction and application and further accelerate the implementation and application of AI Agents.
Of course, at a time when agents have become the main theme of AI applications, the more exciting thing around the Spring Festival is still the AI Agent industry. Global technology manufacturers are constantly engaged in product development and ecological expansion.
Google released the new multimodal model Gemini 2.0 in December 2024. Its performance has been comprehensively improved and supports multimodal input and output such as pictures, video and audio. Based on the Gemini 2.0 architecture, Google has launched three new AI agent prototypes: General Large Model Assistant Project Astra, Browser Assistant Project Mariner, and Programming Assistant Jules. Among them, programming assistant Jules can directly integrate into GitHub’s workflow system to analyze complex code bases and implement fixes.
In October 2024, Microsoft announced the integration of 10 autonomous AI Agents in Dynamics 365. These agents can automate business processes such as customer service, sales, finance, and warehousing. These AI Agents support OpenAI’s o1 model, have independent learning capabilities, and can automatically perform ultra-complex services across platforms. For example, Lumen, a well-known American telecommunications company, can save US$50 million in annual costs through AI Agents, which is equivalent to adding 187 full-time workers.
OpenAI released its first AI Agent Operator on January 24, 2025. The system can automatically perform a variety of complex operations, including writing code, booking travel, and automated e-commerce shopping. On February 2, the Deep research function of agent products for the field of in-depth research was officially launched. This function can complete professional reports in 5-30 minutes. It supports high-intensity knowledge workers in multiple fields. It is supported by the o3 model. It uses end-to-end intensive learning and training. It is working collaboratively by four modules. It has been launched in ChatGPT. In the future, it is planned to expand data sources and operators to perform complex tasks.
Anthropic released an Agent Best Practices Guide in January 2025, aiming to improve the efficiency and flexibility of AI Agents in multiple application scenarios. It is also planned to launch a virtual AI collaborator in 2025, capable of writing and testing code. Its flagship product Claude 3.5 Sonnet upgrade ranked first among AI models in the OSWorld test in computer usability.
In China, Alibaba Yuntong Yiqian also launched the ultra-large MoE model Qwen2.5-Max on January 29. The model’s pre-training data exceeds 20 trillion tokens, performs well in multiple benchmarks, and its overall performance is better than DeepSeek V3.
Tongyi Qianwen also open-source a new visual model Qwen2.5-VL, launching three size versions in 3B, 7B and 72B. Qwen2.5-VL and 2.5MAX have not only achieved significant improvements in performance, but also demonstrated strong application potential in AI Agents, especially computer uses. For example, Qwen2.5-VL can directly operate as a visual Agent, reason and dynamically use tools, supporting multi-step complex tasks on computers and mobile phones, such as automatically querying weather, booking air tickets, sending messages, etc.
Major technology companies are using fast-iterative products and solutions to externally demonstrate their absolute speed of development in the field of AI Agents. Judging from the current performance in various fields, in 2025, the first year of commercial application of AI Agents, the implementation of agents will be much faster than everyone imagined, indicating that AI Agent technology is about to usher in explosive growth. Of course, the competition is also more intense.
In this case, naturally many friends want to quickly recognize and master AI Agents. The fastest way to understand an industry is to start by reading various industry research reports.
In order to help everyone better understand, learn and apply AI Agents, Wang Jiwei Channel carefully prepared 10 research reports on the agent industry on the first day of construction after the Spring Festival holiday in 2025.
These research reports cover the latest technological progress, application scenarios, industry trends and challenges faced by AI Agents, and aim to provide comprehensive and in-depth reference for everyone. Whether you are enterprise decision makers, technology developers or readers interested in AI Agents, you can obtain valuable information from these research reports and seize the development opportunities brought by AI Agents.
Report 1: Google Agents White Paper
The white paper explores how Generative AI models can expand their capabilities by using external tools to form so-called Agents. It introduces in detail the definition, cognitive architecture, key components, tool use, and how these tools and architectures can be used to enhance model performance and realize production applications.

It first clarifies that the key to distinguishing agents from pure models is that they can use tools to access external information and conduct autonomous reasoning and action planning, rather than just relying on training data for a single prediction.
The white paper details the three core components of an Agent: the Language Model, Tools (Extensions, Functions, Data Stores), and the Orchestration Layer. The choreography layer uses various reasoning frameworks (such as ReAct, Chain-of-Thoughts, Tree-of-Thoughts) to guide the Agent’s decision-making process. Tools give Agents the ability to interact with the outside world: Extensions connect Agents and APIs, Functions allow clients to control API calls, and Data Stores provide access to external data and support applications such as RAG.
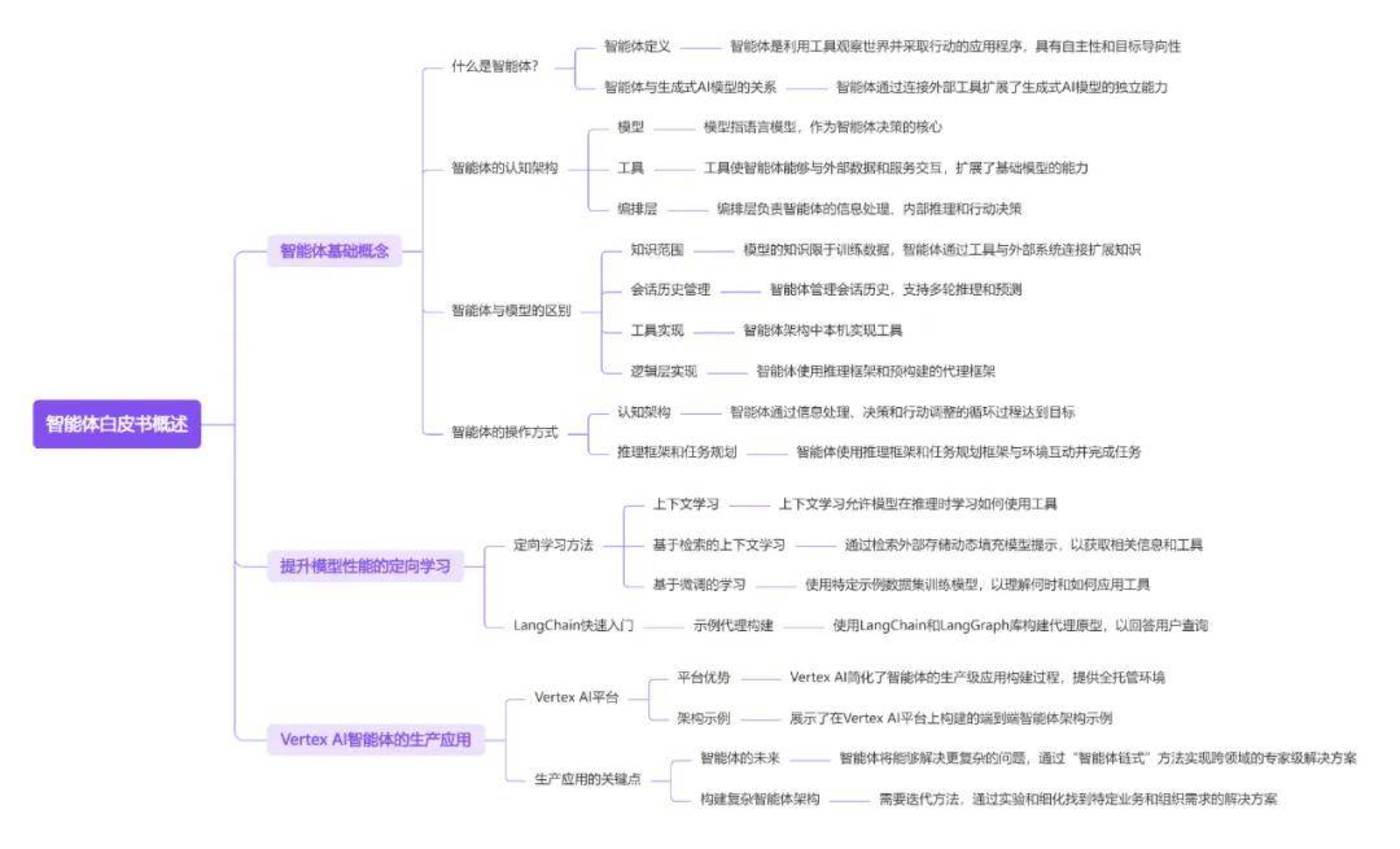
Finally, we introduce methods of building and deploying agents on LangChain and Vertex AI platforms, and discuss how to improve model performance through various learning methods such as context learning, retrieval-based context learning, and fine-tuning. All in all, this white paper aims to systematically explain the principles, architecture and application practices of generative AI Agents, and provide guidance for developers to build more powerful and flexible AI systems.
It is a very valuable resource for friends who want to understand or build the Agents system. I recommend studying it in detail.
Report 2: Anthropic “Building effective agents”
“Building effective agents” provides an in-depth discussion of practical experience and insights in building large language model (LLM) agents. At the beginning of the article, the word Agent is clearly defined and the architectural differences between Workflow and Agent are carefully distinguished.

Workflow refers to the orchestration of predefined processes of LLM and tools, while Agents give LLM the flexibility to dynamically regulate its processes and tool use. It also analyzes the situation and how to effectively use the Agent system, and emphasizes that during the application construction process, the most concise solution should be given priority, and complex functions should be gradually introduced according to actual needs.
The article explores in depth several common patterns for building agents, including enhanced LLM, Prompt Chaining, Routing, Parallelization, Orchestrator-Workers, and Evaluator-Optimizer, and emphasizes the importance of brevity, transparency, and thorough tool documentation and testing.
These patterns are designed to guide developers in building Agent systems that are efficient, reliable, and easy to maintain, rather than pursuing overly complex systems. The article also provides practical cases of using Agents in the areas of customer support and coding, and details the tool’s hinting engineering techniques in an appendix to help developers create more effective Agent-Computer Interfaces (ACI).
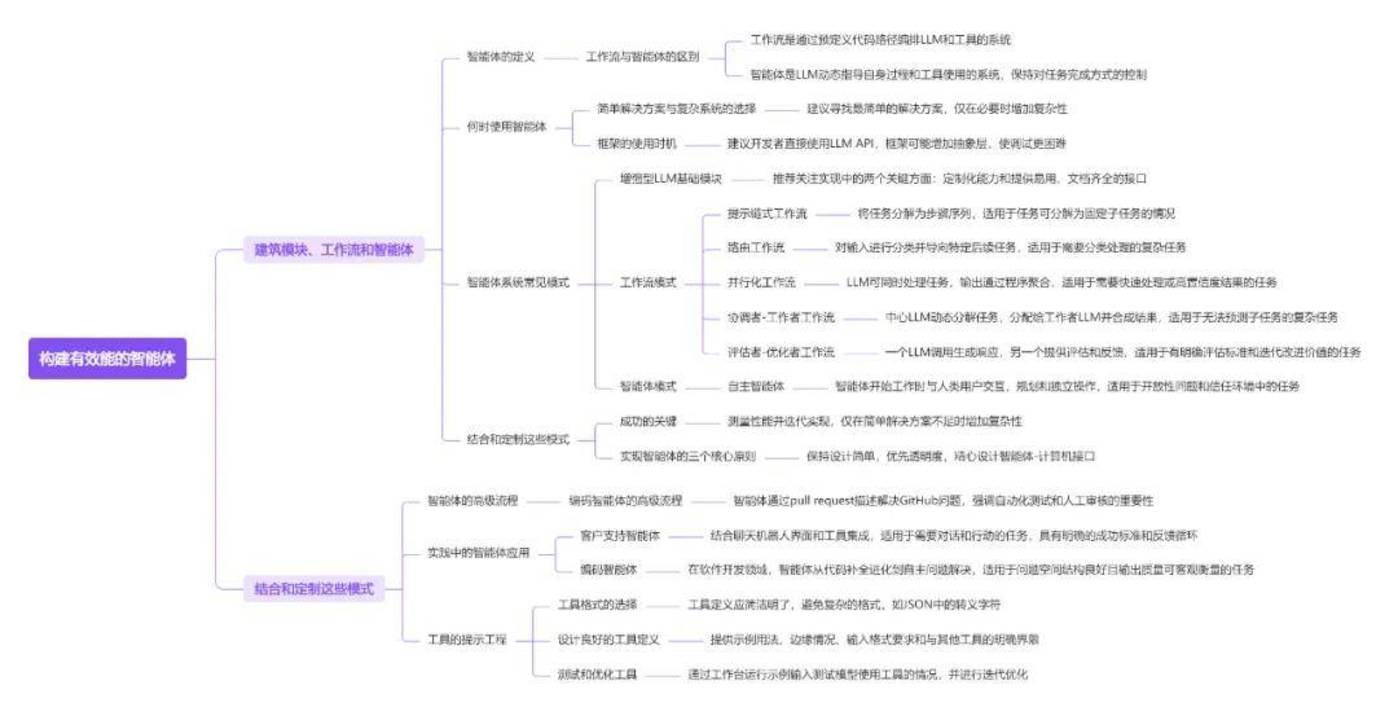
In addition, the article introduces a variety of frameworks. Although these frameworks simplify the implementation process, they may also bring additional layers of abstraction and affect debugging. Therefore, the article recommends that developers use the LLM API directly and use the framework when necessary, while ensuring that they understand the underlying code. The ultimate goal is to ensure that the design of the Agent system remains concise, prioritizes transparency, and carefully design the Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) through tool documentation and testing.
The “Building effective agents” report provides comprehensive and practical guidance to readers interested in AI agents. It not only explains the core concepts and construction methods of AI Agents, but also helps readers better understand and apply these technologies through practical cases and suggestions. This report is a rare reference for readers who want to understand and build LLM Agents in depth.
Report 3: LangChain, State of AI Agents
By surveying more than 1300 professionals, the report reveals the current use status of AI agents in 2024, including their application in different industries, main uses, challenges they face and future development trends.

The report defines an AI Agent as a system that uses a large language model (LLM) to determine the flow of application control. This paper discusses different types of Agent frameworks, such as ReAct, Multi-Agent Orchestrator, LangGraph, etc., which have attracted widespread attention in the industry. Mentioned the application of AI Agents in different industries, as well as their specific uses in handling research, summary, personal productivity tasks, customer service, etc.
The report found that more than half of respondents are using artificial intelligence agents in production environments, and the vast majority of respondents plan to deploy AI agents in the near future. The main application cases include information research and summary and improving personal productivity, while customer service is also an important area. The report emphasizes the importance of tracing and observability tools and human supervision in controlling AI Agent risks, and points out that performance quality is the biggest obstacle to deploying AI agents.
Finally, the report analyzes success cases such as Cursor, Perplexity, and Replit, and explores emerging topics such as multi-step task management, repetitive task automation, and AI agent collaboration. The report’s survey shows that companies of different sizes differ in their control and priorities for AI Agents. Large companies pay more attention to security and compliance, while small companies pay more attention to tracking and understanding results.

The LangChain AI Agent Status Report provides a comprehensive overview of the current status of AI agents and provides an in-depth discussion of their application scenarios, challenges and future trends. It has high reference value for readers who want to understand AI Agent technology and deploy related applications in practice.
Report 4: Langbase “2024 State of AI Agents”
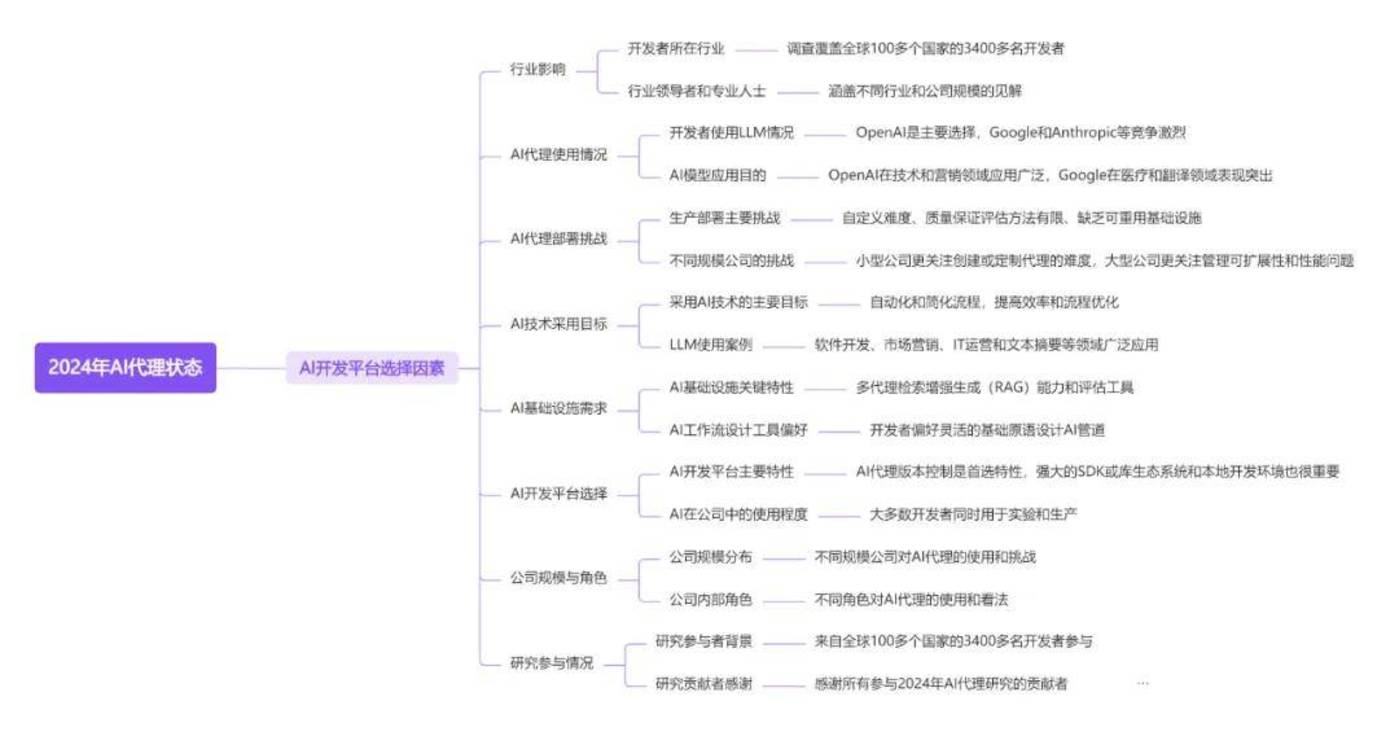
Langbase Research’s “State of AI Agents” summarizes the latest trends in the field of AI agents based on feedback from more than 3400 developers from more than 100 countries. The report describes the new peak of AI technology in 2024, how developers are using different large language model (LLM) providers to build AI agents, and discusses the challenges and goals faced by adopting AI agents in their workflows.

The research aims to understand the development of AI Agents in 2024, including how developers use different LLM provider services, as well as the challenges and goals encountered in practical applications. The study also explored the use of AI in different industries and company sizes, as well as developers ‘preferences for AI development platforms.
The report reveals that OpenAI dominates LLM providers, but Google and Anthropic are close behind; different LLM providers have advantages in different industry applications. Scalability, complexity and data privacy are two major factors that hinder the widespread use of AI agents, and accuracy is the primary consideration for developers when choosing LLM.
The report also pointed out that automation and simplification are the primary goals for enterprises to adopt AI technology, and software development is the main application area of LLM. Finally, the report highlights developers ‘need for customizable AI development platforms and tools, as well as the importance they attach to version control and SDK ecosystems.
For readers who want to understand AI Agent technology, this is a very valuable reference material, which can help you better understand market dynamics and technology development direction.
Report 5: Insight Partners,”The state of the AI Agents ecosystem: The tech, use cases, and economics”
This report by Insight Partners explores the current status, use cases and economic models of the AI Agent ecosystem. Based on interviews with builders, enterprises and researchers, this paper analyzes the actual deployment of AI Agents in enterprise architecture, discusses the complexity of different use cases, the trade-offs between purchasing specific functional agents and building custom Agent workflows, and the diversity of value measurement and attribution

The report first defines the AI Agent and explains key considerations in its architectural design, especially the human-machine collaboration cycle and mission planning strategies. The report then provides an in-depth analysis of the reference architecture of AI Agents, including data retrieval (RAG, memory, long context), Agent computer interfaces (function/tool calls, computer usage, integration), and performance evaluation and security protection (Guardtrails).
The report divides the types of AI agents, including vertical agents, horizontal Agent platforms, multimodal agents and classic SaaS Agent interfaces. The report also maps the AI Agent market, points out opportunities for infrastructure and vertical platforms, and discusses decision-making considerations for building and purchasing AI Agents, as well as emerging pricing models (platform + hire Agent, platform + result-oriented pricing, pure result-oriented pricing).
Finally, the report summarizes the challenges and best practices faced by enterprises and builders in the deployment and development of AI Agents, emphasizing important aspects such as compliance, data preparation, reliability, ROI measurement, and cultural integration.
The report believes that the research difficulty of AI Agents lies in understanding the complexity of AI Agents, including how they reason and act independently, and how to integrate them into existing enterprise systems. Researchers need to assess the complexity of different use cases and determine the best trade-off point between purchasing a specific feature Agent and building a custom Agent workflow. Diversity in measuring and attributing values is also a challenge, as different companies may have different evaluation criteria and business goals.
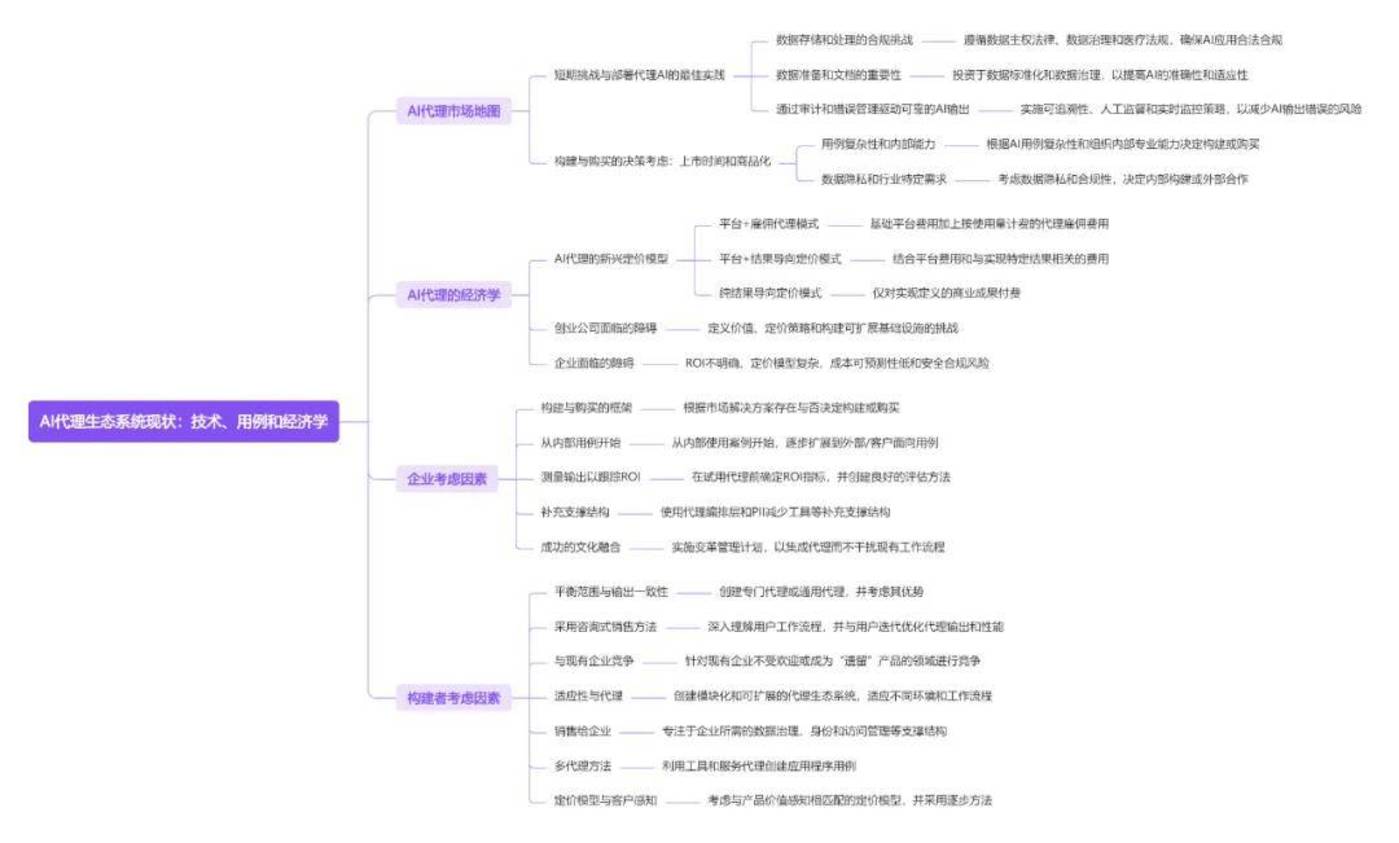
This report aims to provide enterprises and AI Agent builders with a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the AI Agent ecosystem and provide guidance on their development strategies. It not only analyzes the technical details of AI Agents, but also discusses in depth the practical issues that enterprises need to consider when deploying AI Agents, and provides valuable suggestions for builders, which are recommended to study carefully.
Report 6: infoQ “Al Agent Application Research Report in China”
The “2024 China AI Agent Application Research Report” released by InfoQ Research provides an in-depth analysis of the market development background, characteristics, application cases and future trends of AI Agents in China. Based on indicators such as the number of technology patents, technology development time, and technology public opinion index, combined with data such as market size and financing events, the report draws a maturity model for AI Agent applications in China in 2024, and discusses the application status and future development direction of AI Agents in different fields.

The report focuses on research on AI Agent applications in China in the second quarter of 2024. The report first analyzes the background and characteristics of the AI Agent market, as well as the current technology maturity model of artificial intelligence in China, with special emphasis on the role of AI Agents as a bridge connecting the large model and the application layer.
The report provides an in-depth discussion of the market trends of AI Agents, including the collaborative development of single/multiple agents, common technology frameworks, typical application scenarios (life, enterprise professional), and product strategies of different manufacturers (large-model startups, Internet technology vendors, RPA vendors, digital enterprise service providers). It also looks forward to the future development trends of AI Agents, such as the improvement of large model capabilities, the improvement of tool ecosystems, multi-agent collaboration, and the changes that the rise of terminal agents (mobile phones, computers, etc.) will bring.
The report pointed out that AI Agents, as an important supplement connecting the model layer and the application layer, are gradually deepening into complex tasks and demonstrating application potential in multiple industry scenarios. Based on core indicators such as the number of technology patents, technology development time, and technology public opinion index, combined with public information such as market size and financing events, as well as verification by technical and market experts, the report draws a China artificial intelligence maturity model, and analyzes the market characteristics, application scenarios, product development, profit models, etc. of AI Agents are discussed in detail.
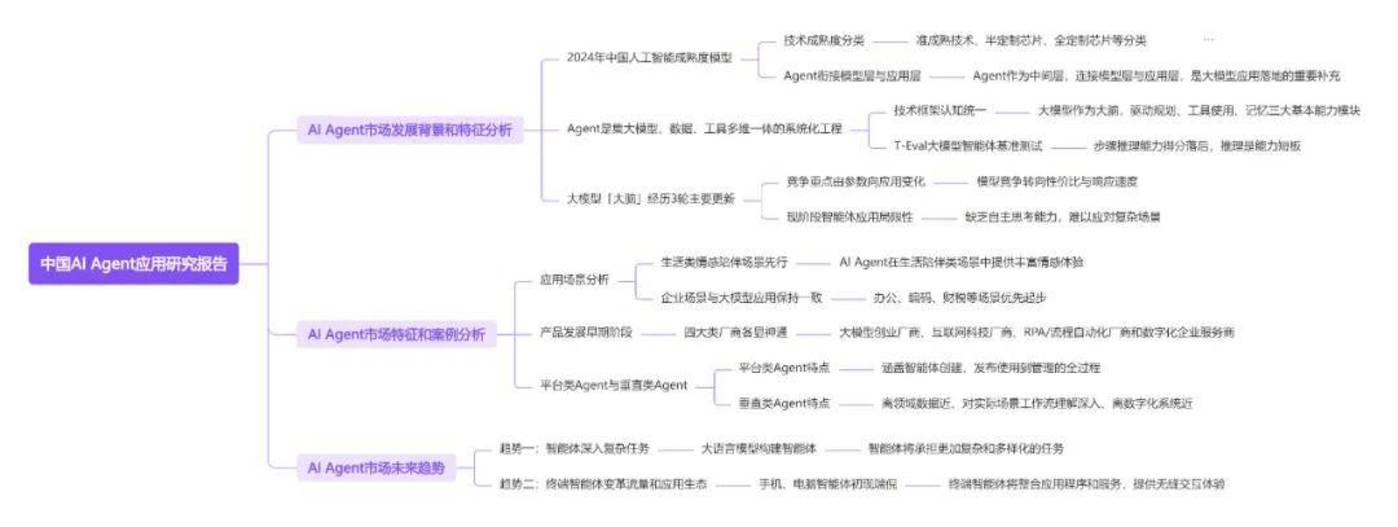
The “2024 China AI Agent Application Research Report” is a very forward-looking and in-depth research report. It is of great reference value for practitioners, corporate decision makers, technology enthusiasts and researchers who pay attention to the development of artificial intelligence technology, especially AI Agent applications.
Report 7: Love Analytics “2024 Love Analytics AI Agent Application Practice Report”
The “2024 Love Analysis AI Agent Application Practice Report” was written by Love Analysis and aims to discuss the application status, market insights and future development trends of AI Agents in enterprises.

The report first outlines the core capabilities of AI Agents, independent thinking, independent execution, and continuous iteration, as well as its rise in the market and the main challenges for enterprise implementation: difficulty in implementation and difficulty in application.
The core content focuses on two specific markets: data analysis AI Agent and AI Agent development and management platform, and analyzes the key points and success cases of their implementation. For example, city commercial banks use data analysis AI Agent to improve data analysis efficiency, and Feihe uses AI Agent development management platform promotes digital transformation.
The report pointed out that AI Agents, as an intelligent application that can sense the environment, make decisions based on goals, and perform actions, have made a qualitative leap with the enhancement of large model capabilities and the maturity of related technologies. The report emphasizes the three core capabilities of AI Agents in enterprises: independent thinking, independent execution, and continuous iteration, and analyzes the challenges faced by enterprises when implementing AI Agent projects.
The report also pays special attention to the data analysis AI Agent market and the AI Agent development and management platform market, providing market insights and case analyses, and providing strategic guidance and practical insights for enterprises.
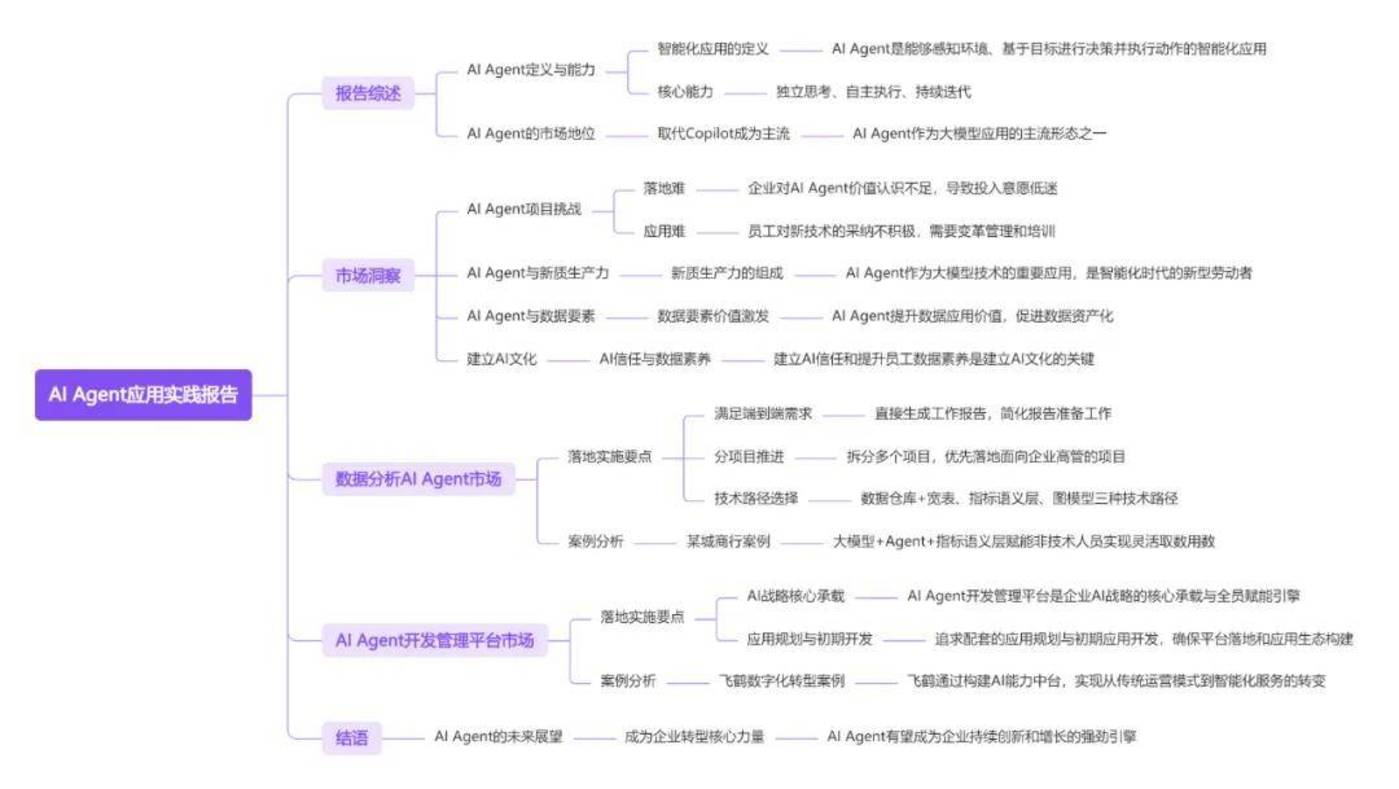
The report not only analyzes the technology and applications of AI Agents, but also discusses in depth the challenges and coping strategies faced by enterprises when implementing AI Agents. The report emphasizes that enterprises should proceed from their own characteristics, establish the intrinsic connection between AI Agents and new productivity and data elements, realize value sublimation, and establish AI culture. This report is suitable for corporate decision makers, IT leaders, and readers interested in AI Agent applications.
Report 8: Toubao Research “2024 China AI Agent Industry Research”
The report “2024 China AI Agent Industry Research: Agents Implement Thousands of Industries, a New Engine Leading the Intelligent Revolution” was released by Toubao Research Institute and provides an in-depth analysis of the development status, application prospects, market trends and industry ecology of AI Agents (Artificial Agents) in China.

The report first defines AI Agents and distinguishes them from large models, emphasizing their autonomous decision-making and execution capabilities; then, it analyzes the key characteristics, classification and development history of AI Agents, and conducts an inventory of mainstream projects and products at home and abroad; Then, the report discusses the market size, driving factors and industry ecological map of AI Agents, pointing out that it has broader prospects in enterprise-level applications (toB); Finally, the report provides an in-depth analysis of the application and development trends of AI Agents in different industry fields, and predicts the future development direction. In particular, it points out that the financial industry is the most mature field for AI Agent applications, while the government field is due to data acquisition. Limited, development is relatively lagging behind. All in all, the report aims to provide investors, companies and researchers with a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of China’s AI Agent industry.
The report pointed out that AI Agents, as an intelligent entity that can perceive the environment, make decisions and perform actions, have stronger autonomy and adaptability than traditional artificial intelligence. It introduces in detail the definition, infrastructure, feature classification, development history, market driving factors, industry application map, business model and comparison between consumer-level and enterprise-level applications of AI Agent.
It also predicts the application development of AI Agents in different industries, and provides an inventory of AI Agent projects and products at home and abroad. Overall, AI Agents have broad prospects in enterprise-level applications, especially in industries such as finance, e-commerce retail, education, medical care, manufacturing, transportation, media entertainment, energy, logistics and government affairs. potential.

The report not only points out the mature applications of AI Agents in fields such as finance, but also explores its potential in other industries, providing a valuable reference for readers interested in AI Agent technology and the market. This report is suitable for readers who want to understand how AI Agents can be implemented and lead industry change.
Report 9: Letta,”The AI Agents Stack”
This article “The AI agents stack” discusses the latest developments in the AI Agent stack, especially the AI Agent ecosystem at the end of 2024, including three key levels: Agents hosting/services, Agents framework, and Large Language Model (LLM) model and storage. Based on the authors ‘more than one year of working experience in the open source AI field and more than seven years of AI research experience, the report questioned the existing Agents technology stack classification and shared their own Agents technology stack model.

The report explores the software ecosystem of AI agents at the end of 2024 and proposes the author’s own agent stack model based on years of experience.
The model divides the agent system into three layers: the bottom layer is the Large Language Model (LLM) and its services and storage, including various API services and vector databases; the middle layer is the agent framework, which is responsible for LLM calls, state management, memory management and multi-agent communication; the top layer is agent hosting and services, focusing on how to deploy agents as services and access them through REST APIs.
The report emphasizes that agent development faces greater engineering challenges, such as state management and tool execution, than simple LLM chat bots. The author believes that future agents will be deployed as services and looks forward to the emergence of an industry-standard agent API similar to the OpenAI ChatCompletion API.
The report also mentions the emergence of LLM frameworks and SDKs in 2022 and 2023, such as LangChain and LlamaIndex, as well as standard platforms for consuming LLM through APIs, such as vLLM and Olama. At the same time, the article also pointed out the transformation of the concept of Agents in the AI field in 2024 and the necessity of how to develop from LLM to AI Agents.
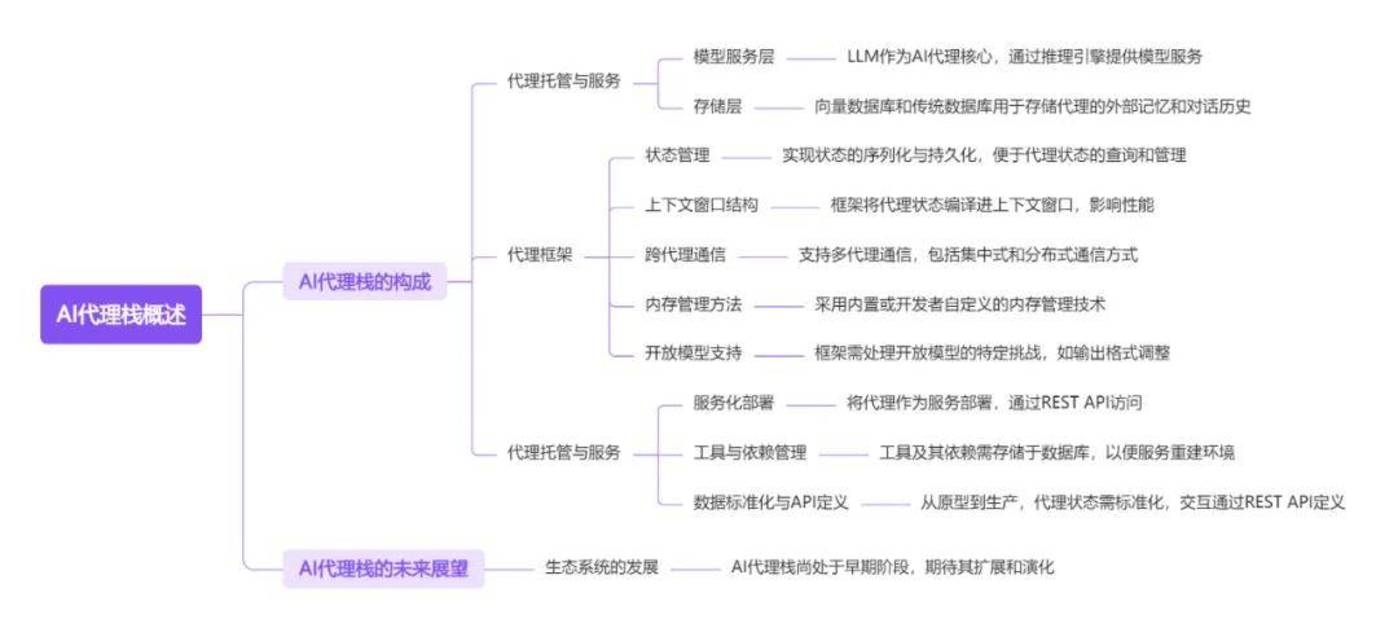
This report is mainly aimed at software developers and aims to help them understand the complexity of the AI Agent technology stack and provide them with guidance on building vertical Agent applications. The report highlights the engineering differences between AI Agents and traditional LLM chat bots, and introduces relevant resources provided by Letta. This report is suitable for developers interested in AI Agent technology stacks and practical applications.
Report 10: Deloitte, Prompt for action How AI agents are reshaping the future of work
The report, released by Deloitte’s Institute for Artificial Intelligence, explores how AI agents and multi-agent systems can reshape future work. It focuses on the scalability capabilities of generative AI (GenAI) and the synergy of multi-agent AI systems, and how these technologies affect enterprises and drive the transformation of intelligent organizations.

The report discusses in detail how companies can use AI Agents and multi-agent AI systems to reshape business processes, improve efficiency and achieve automation with the rapid development of AI technology.
The report pointed out that AI agents are different from traditional language models in that they have the ability to reason, plan, remember and act, and can automate work processes. Multi-agent systems improve efficiency, learning ability and accuracy through collaborative cooperation, and handle complex tasks. For example, applications in strategic insights demonstrate their advantages in speed, efficiency and scalability. It also explores the impact of AI agents on strategy, risk, talent and business processes, and recommends leaders assess use cases, develop strategic roadmaps, invest in infrastructure and talent development, and strengthen data governance and risk management.
The report mentions large language models (LLMs) and GenAI tools that are currently widely used by enterprises. Although these tools can generate output based on simple prompts, their interactions are usually transactional and have limited scope of action. This paper discusses the differences between AI Agents and traditional language models, and how AI Agents achieve goals by understanding context, planning workflow, connecting external tools and data, and executing actions, thereby overcoming the limitations of traditional AI applications.

The report believes that how to overcome the limitations of traditional AI applications in understanding complex requests, planning workflows and executing multi-step tasks, and how to integrate different AI Agents to achieve higher levels of automation and optimization are key issues that need attention.
Overall, the report highlights the potential of AI agents and multi-agent systems in driving intelligent transformation, and points out that forward-looking companies and government agencies have begun to deploy these technologies, suitable for readers interested in the latest developments in AI agents and their practical applications in various industries.



