Generative AI protocols can enable individuals to become outstanding artists and open doors to careers that were previously inaccessible.
Written by: Kava Labs

We will continue to discuss in depth the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology, focusing on the role of generative AI and tokenization. As one of the most innovative yet controversial areas of AI and blockchain technology, we need to refer to previous articles on RWA tokenization, natural language processing (NLP) in AI, AI’s role in risk mitigation and cross-chain interoperability to fully understand the broader impact of the convergence of these two technologies.
In this article, we will discuss the power of generative AI, how it works, and the copyright material issues we face when tokenizing the content output by generative AI. We will then turn to the role of blockchain technology and non-homogeneous tokens (NFT) as potential solutions to these issues. We will also look at industries that are already leveraging NFT and end the article by discussing the future potential of this dynamic field and the role AI may play.
Creating the future of content
Like other aspects of the AI field, the evolution of generative AI has deep roots in computer science, dating back to the 1960s. British artist Harold Cohen achieved early iterations of computer image generation at the University of California, San Diego through his AARON project. However, despite these early iterations of generative AI imaging, it was not until the launch of ChatGPT 3.5 at the end of the fourth quarter of 2022 that marked the prosperity of modern AI and gave the general public access to this epoch-making technology.
With the release of Midjourney, Leonardo.ai and DALL-E in 2023, the popularity of generative image protocols has exploded rapidly, Generative AI (GenAI) and prompt engineering have quickly entered the public eye, and Large Language Models (LLMs) have also attracted much attention. Overnight, everyone gained the ability to generate realistic images in seconds, a work that previously required a lot of labor and could only be done by professional artists and photographers.
Since then, generative AI has come a long way, constantly iterating and improving earlier versions. Even traditional Web2 companies have begun to implement AI image generation and editing protocols, such as Photoshop, which launched its generative fill kit in May 2023. We have also witnessed the expansion of the field from images to audio, video and 3D modeling.
How does generative AI work? Should traditional artists need to worry, and how blockchain can help generative AI?
understand the technology
To determine where blockchain may meet with generative AI, we first need to understand how the technology works and whether it could be interpreted as plagiarism.
The first step in generative AI is to collect, index, and clean raw data the same as other AI models. Generative AI collects images, audio samples, videos, or 3D digital models. The model can then be trained to recognize objects, textures, colors and audio patterns.
Once the model breaks down its sample data into its most basic components, it can be used to reconstruct and replicate patterns and dependencies, such as how colors interact and the spatial relationships between objects. Similar to the way large language models use probability models to predict the next word, sentence, or paragraph, generative AI uses probability models to predict pixel values and their positional relationships to each other, and combine them into a single coherent image output.
The final stage of generative AI is to use these outputs in its feedback loop. By iterating and improving the model, more accurate output is created over time.
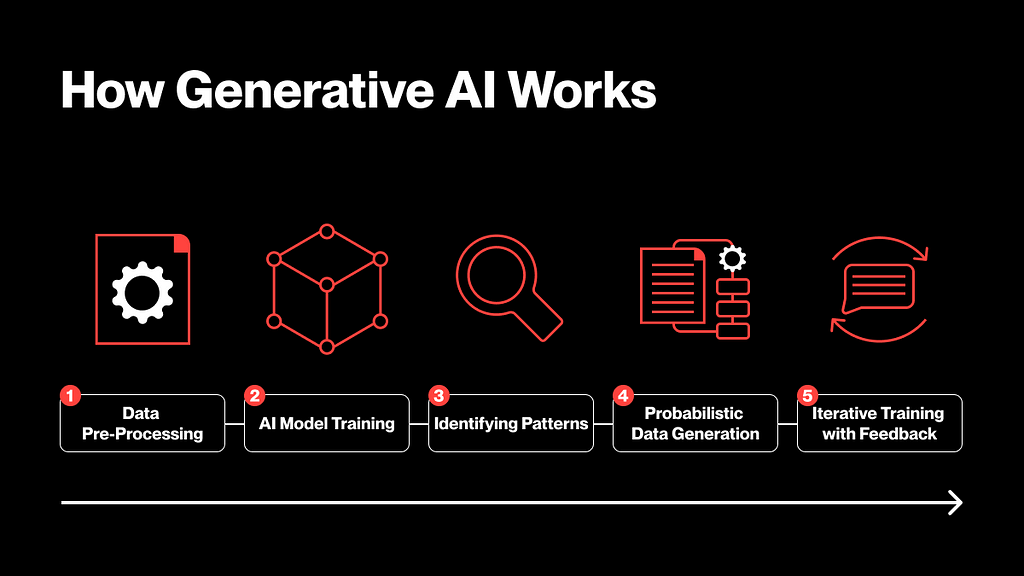
Disputes over copyright began to blur because models could be trained on open source data and would not directly copy any single raw data for copying. They use highly complex predictive models based on billions of raw data touchpoints and combine them into one output through predictive modeling. One way to think about it is that these models are more like modern singers might be influenced or inspired by Michael Jackson or the Beatles, rather than directly covering their songs.
The rise of NFT
NFT first appeared in 2014, when digital artists Jennifer and Kevin McCoy first cast Quantum on the Namecoin blockchain. In 2017, with the release of CryptoKitties, NFT began to gain niche followers in this field and became popular in the 2021 bull market with projects such as Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks, and independent digital artists like Beeple.
In the bull market in 2021, NFT demonstrated the power of its underlying blockchain technology use cases. Immutable decentralized ledgers can solve the long-standing problem of establishing consistent proof of origin. By having a permanent and unchangeable digital certification seal, industries can easily determine the legal ownership of their products. Artory, a high-end art database, has performed well in using blockchain technology to establish proof of origin for exclusive art.
Since the peak of the NFT craze in 2021, although NFT’s popularity has declined, its importance has not diminished. The introduction of dynamic and non-semi-homogeneous NFT projects through the ERC-721 and ERC-1155 token standards has created new markets with the rise of physical assets (RWAs). Tokenization of physical assets, particularly in the real estate and automotive industries, benefits from the ability to establish consistent proof of origin, while updating the NFT over time to reflect maintenance and improvements.
Casting NFT
NFT became popular in the bull market in 2021, thanks to the convenience of casting the NFT series. For a fast-growing industry with a relatively niche and technology barriers to entry, being able to cast NFTs on platforms such as OpenSea and Rarible provides a simple entry point for millions of users. Setting up a wallet can be more challenging than creating your own NFT series.
Initial setup is done through a simple account creation process. Afterwards, once users connect their wallets to their accounts, they can easily upload and cast a series in minutes, similar to the convenience of uploading images to a cloud provider. The user experience is unmatched, and once their images are reviewed, they can easily trade between the platform and the exchange of their choice.
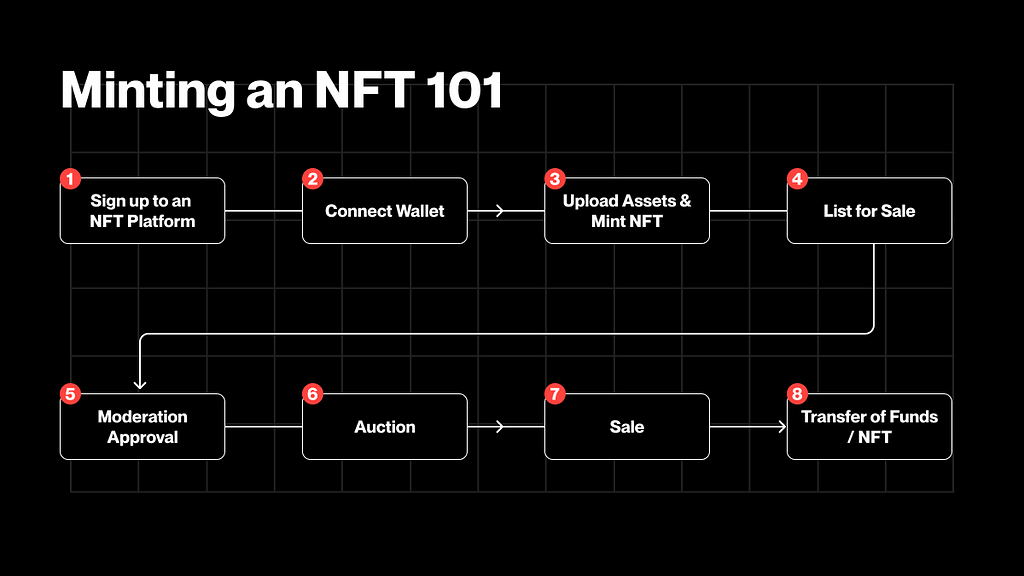
The mobility of digital art
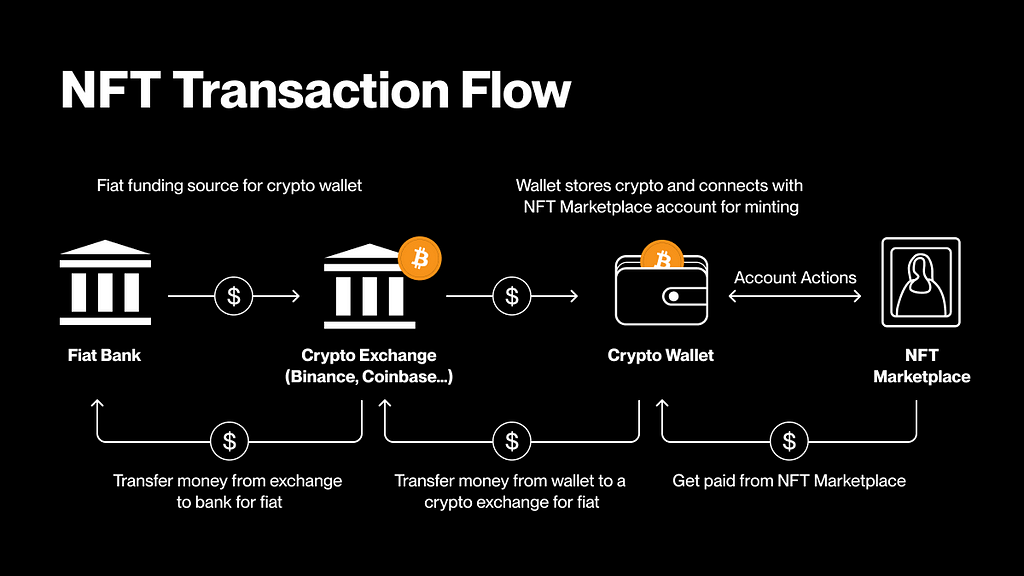
Forging NFT and the ability to freely buy and sell digital art is an important step in attracting millions of users to join. While this is a crash course on the volatility of the cryptocurrency market, more importantly, it provides users with a dynamic educational tool. They quickly understood and began implementing cryptocurrency transactions. For example, it can be seamlessly transferred from NFT platforms to wallets and exchanges, and then converted back into fiat currency.
This has also enabled many creators to monetize their digital art for the first time. This reflects Web3 ‘s basic promise to return financial and creative sovereignty to individuals, rather than third-party gatekeepers.
A new era of royalties
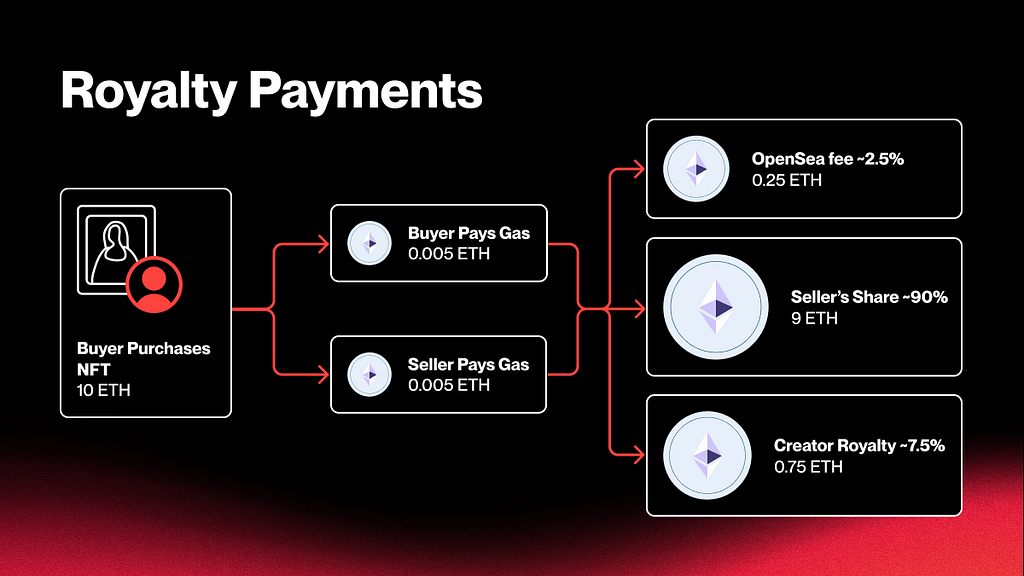
One aspect of NFT that is often overlooked when it comes to establishing the origin of digital assets is its ability to automatically pay royalties to the original creator. Although the concept of Artist Resale Rights (ARR), or droit de suite, has existed since it was first introduced in France in 1920 in the early 20th century, it is still a relatively new practice for many countries.
In this regard, the NFT provides a unique opportunity. For any given NFT transaction, the process of automatically enforcing royalties solves this problem without the need for any cumbersome traditional intermediaries. The NFT platform’s curatorial process returns this power directly to creators, allowing them to determine the percentage of royalties they wish to receive.
The future of AI and NFT
One of the impressive things about the rise of NFT in 2021 is that its rise did not rely on generative AI protocols. In that environment, digital artists flourished, but now anyone can create high-production value art as easily as using a chat robot, so the future profitability of this market is unclear. People may pay more attention to the practicality and community of the project.
Generative AI protocols can enable individuals to become outstanding artists and open doors to careers that were previously inaccessible. However, one of the major problems artists encountered during the previous cycle was the fact that their art was sold as NFT without consent. There is still legal ambiguity about the monetization of digital assets created through generative AI protocols. These two factors can conflict, especially if generative AI assets are used to create generational wealth through the popular NFT series.
In the previous cycle, when NFT was replicated and minted on multiple blockchains, plagiarism also played a role in fueling the flames. The topics of lack of interoperability and data silos have been discussed in previous blog posts. In this regard, AI can play an important role. Through security enhancements such as early anomaly detection and fraud prevention, AI can be the backing it does in the RWA and DeFi spaces. This is critical to establishing cross-chain interoperability security when determining the origin of digital assets.
Welcome to join the official social community of Shenchao TechFlow
Telegram subscription group: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowDaily
Official Twitter account: www.gushiio.com/TechFlowPost
Twitter英文账号:https://www.gushiio.com/DeFlow_Intern



