Today, we take stock of the top ten encryption security incidents in the past (including the Bybit theft incident in February 2025). These incidents cover a variety of complex attack methods from smart contract vulnerabilities to private key leaks and database attacks.
author| huohuo
produced| Vernacular blockchain
On Saturday, the world’s second-largest CEX Bybit was hacked and a total of US$1.46 billion in ETH was stolen, setting a record for a single token theft in history. On February 24, cryptographic financial card service provider Infini was also hacked, and approximately $49.5 million in funds were stolen from its Ethereum address. This series of security incidents has made the already depressed encryption market even worse. It not only exposed that the encryption platform is still not rigorous enough in asset security management, but also further weakened market liquidity. Security issues have once again become the focus of the industry.
It can be said that cryptographic security incidents have occurred frequently in recent years, involving multiple targets such as CEX, DeFi platforms and cross-chain bridges. According to a report from blockchain analysis company Chainalysis, hackers stole approximately US$2.2 billion in cryptographic assets in 2024. So far, the cumulative amount stolen has exceeded US$5 billion (approximately more than 36 billion yuan).
Today, we take stock of the top ten encryption security incidents in the past (including the Bybit theft incident in February 2025). The 36 billion yuan in assets lost in these ten security incidents is a “bloody and tearful lesson” for the owner, but for individuals, What important tips can we get from it to protect encrypted assets?
01. Top 10 Encryption Security Events
The figure below shows the top ten encryption security incidents sorted by the amount of loss. These incidents cover a variety of complex attack methods from smart contract vulnerabilities to private key leaks and database attacks.
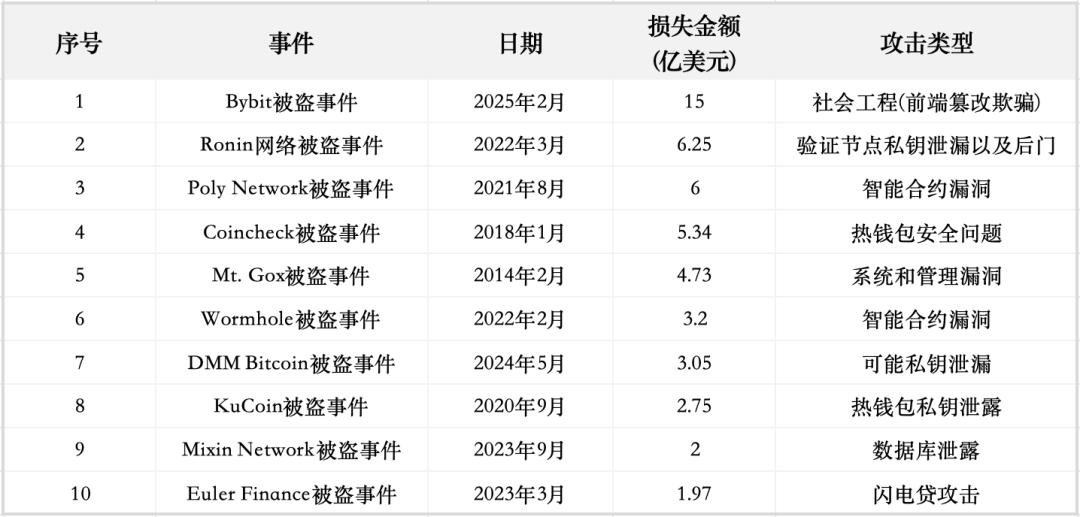
Through analysis, we can see that these theft incidents not only expose specific security loopholes, but also reflect the weak links in technical protection and risk management in the encryption industry.
Next, we will classify and analyze these incidents based on the reasons for their occurrence and the lessons they bring, so as to better understand the security risks behind them and provide reference for future prevention.
1) Wallet private key or security issues
- Ronin network theft (March 2022):$625 million
Ronin Networks is an extended solution specifically designed for blockchain games and NFT, created by Axie Infinity development team Sky Mavis, to address Ethereum’s limitations in transaction fees and processing speeds.
In March 2022, the Ronin network was attacked by the North Korean-backed hacker group Lazarus Group, losing approximately US$625 million in Ethereum and USDC. The hacker successfully controlled five nodes by attacking the network’s verification nodes, allowing him to create and sign malicious transactions and ultimately transfer funds to addresses he controlled.
- Coincheck theft (January 2018):$534 million
Coincheck is one of the more well-known CEXs in the Japanese crypto market. It was established in 2012 and is committed to providing safe and convenient transaction services.
In January 2018, Coincheck was hacked due to hot wallet security issues and lost approximately US$534 million in NEM tokens.
- DMM Bitcoin theft (May 2024):$305 million
DMM Bitcoin is also a Japanese-based crypto CEX company established in 2018.
In May 2024, DMM Bitcoin was hacked, resulting in the theft of approximately 4500 bitcoins (with a market value of approximately US$305 million at the time). Although the specific method of the attack is still under investigation, according to relevant reports, the leaked private key may be a key factor in the hacking.
- KuCoin theft (September 2020):$275 million
KuCoin is a well-known CEX company in Singapore and was established in 2017.
In September 2020, KuCoin was hacked and lost approximately US$275 million in various encryption tokens. The hacker successfully stole a large amount of assets by obtaining the private key of the CEX hot wallet.
Summarizing these four theft incidents, we can see that they were all stolen because of hot wallets or insufficient node security. Verification nodes and hot wallets are easily targeted by hackers because they are connected to the Internet and are convenient. There are many methods of hacking, including obtaining private keys through malware, phishing attacks or exploiting internal platform vulnerabilities. Once the attack is successful, hackers can quickly transfer assets, causing irreparable losses. Relatively speaking, storage locations such as cold wallets that are not connected to the Internet can effectively avoid the risk of online attacks and become a relatively safer choice for storing encrypted assets.
In addition, for CEX, ensuring strict management and storage security of private keys is the key to preventing large-scale capital theft; for individual users, proper custody of private keys also determines the security of assets. Once the private key is lost or leaked, the user will completely lose control of the assets because no third party can help retrieve the funds. Therefore, both CEX and individuals need to establish better key protection measures to reduce security risks.
2) Smart contract vulnerability
- Poly Network theft (August 2021):$600 million
Poly Network is a cross-chain protocol that allows users to seamlessly transfer and exchange assets between multiple blockchain platforms, enabling cross-chain transactions and collaborative work.
In August 2021, the Poly Network Cross-Chain Bridge was hacked due to a smart contract vulnerability, losing approximately US$600 million in various tokens. Hackers used the vulnerability to bypass authority controls and transfer a large number of tokens to their own addresses. However, surprisingly, the hackers then negotiated with the platform and successively returned most of the stolen funds.
- Wormhole theft (February 2022):$320 million
Wormhole is a decentralized cross-chain bridge protocol that allows users to transfer assets between multiple blockchain networks without relying on a single chain ecosystem.
In February 2022, the Wormhole Cross-Chain Bridge was hacked while connecting Solana and the Ethereum blockchain, resulting in the theft of approximately $320 million in packaged Ethereum (wETH). The attacker took advantage of the vulnerability of the cross-chain bridge smart contract, bypassed the verification mechanism, forged a large number of wETH without authorization, and extracted it to his own address.
Security incidents at Poly Network and Wormhole exposed the vulnerability of cross-chain protocols during asset transfer and verification. Especially in the management and verification of cross-chain assets, vulnerabilities are easily exploited by hackers, causing huge losses. This reminds us that the design of cross-chain protocols must pay more attention to authority control in smart contracts to ensure the verification of operations, especially in the management and verification of cross-chain assets.
In order to improve security, cross-chain platforms need to conduct regular comprehensive security audits and vulnerability inspections to discover and fix potential problems in a timely manner. At the same time, it is recommended to introduce a multi-signature mechanism and stricter authority management in contract design to avoid single points of failure or hackers controlling critical permissions. In addition, the update and maintenance of cross-chain protocols should also have strict procedures to ensure that each repair and upgrade is fully tested to improve the security of cross-chain platforms, reduce attack risks, and protect user assets.
3) System vulnerabilities or database leaks
- Mt. Gox theft (February 2014):$473 million
Mt. Gox was once the world’s largest Bitcoin CEX, with transaction volume once accounting for approximately 70% of global Bitcoin transactions. It was established in 2010 and is headquartered in Japan and played a key role in the early boom of the crypto industry.
However, in 2014, the CEX was eventually bankrupt due to multiple security breaches that resulted in the theft of approximately 850,000 bitcoins (valued at approximately US$473 million at the time), becoming one of the most sensational scandals in the history of encryption. The attack exposed problems of insufficient monitoring mechanisms and slow response to suspicious activities, while the hacker’s specific modus operandi has not yet been fully understood.
- Mixin Network theft (September 2023): The $200 million Mixin Network is a decentralized cross-chain protocol designed to solve interoperability issues between blockchains.
In September 2023, the Mixin Network peer-to-peer trading network was hacked due to a cloud service provider’s database leak, resulting in the theft of approximately US$200 million in Bitcoin and Ethereum assets.
These two incidents exposed the serious risks of system vulnerabilities and database leaks in the encryption industry. Mt. The Gox incident highlighted the lack of adequate security monitoring and response mechanisms for encrypted CEX, while the Mixin Network incident reminded us that we must be extra careful when relying on third-party cloud services. In order to avoid similar problems, the platform should strengthen multi-level security protection, establish a complete monitoring and Incident Response Service system, and ensure that cooperation with third-party suppliers has sufficient security guarantees.
When dealing with such incidents, first of all, we should not put all the “eggs” in the same basket; secondly, we also need to pay attention to whether this “basket” has sufficient compensation capacity when a problem occurs. Especially in the crypto space, when choosing CEX or other platforms, you must ensure that they have sufficient reserves and financial health to cope with potentially large losses. At the same time, it is also necessary to evaluate the platform’s risk response mechanism, insurance policies and historical compensation records. After all, risks are sometimes inevitable, and choosing a platform that can take responsibility in times of crisis is also responsible to yourself.
4) Front-end tampering fraud
- Bybit theft (February 2025):$1.5 billion
Bybit is a crypto CEX company established in 2018. It is headquartered in Singapore and mainly provides crypto derivative products.
After being hacked on February 22, 2025, about US$1.5 billion in Ethereum and other related pledged assets were lost. This incident involved cold wallet transaction manipulation. The hacker displayed the correct address through a fraudulent signature interface and changed the underlying smart contract logic to transfer funds to unauthorized addresses. This attack method shows that even cold wallets are not absolutely safe.
Although cold wallets are safer than hot wallets, we have also seen through the Bybit theft incident that security awareness is always the most important. In addition to choosing a CEX with a good security record, wallet management, transaction verification and secure operating processes are also crucial, because cold wallets are not everything.
It is reported that the root cause of this Bybit theft incident is attributed to the Safe multi-signature problem and attack methods. The attacker launched a malicious disguised transaction against Bybit through the damaged Safe developer machine, which suggests that due to insufficient security protection of developer devices and credentials, even if there are no obvious smart contract vulnerabilities or source code issues, they will be hacked.
This reminds us that in addition to choosing a CEX with a good security record, wallet management, transaction verification and secure operating processes are crucial, and developers should strengthen security awareness in every aspect of their machines, credential management and operations. At the same time, users need to be extra cautious when signing transactions and remain highly vigilant to ensure that every step of the operation is not negligent.
5) Lightning loan attack
- Euler Finance theft (March 2023):$197 million
Euler Finance is a decentralized financial platform built on Layer 2 networks such as Ethereum and Optimism. It is committed to providing seamless and efficient debit and loan services.
In March 2023, Euler Finance’s decentralized debit platform suffered a flash loan attack, resulting in the theft of approximately US$197 million in various tokens. Attackers exploit loopholes in the platform’s smart contracts to manipulate market prices through flash loans and trigger the platform’s clearing mechanism, thereby illegally stealing funds.
This incident once again exposed the potential loopholes of decentralized financial platforms in smart contract design and market mechanisms. Flash lending attacks often rely on manipulating market prices and triggering clearing mechanisms, exposing the platform’s weaknesses in price prediction and market stability. In order to deal with such attacks, platforms should focus on reviewing the code of smart contracts, especially in the parts involving market manipulation and clearing mechanisms, and security protection needs to be strengthened.
In addition, safety audits and historical reputation are key factors in assessing project reliability. Even if a project promises high returns, don’t ignore potential risks and avoid falling into traps. Whether you are handing over funds to a centralized platform or using decentralized applications, you need to be cautious and not take it lightly.
02. What safety advice do you give to individual currency holders?
Looking back at these security incidents, it is not difficult to find that CEX security loopholes, mistakes in private key management, and upgrades of hacking methods are all constantly threatening the security of encrypted assets.
These events not only reveal the risks hidden in the world of digital assets, but also provide us with valuable experience. Learning how to identify potential threats and adopt more secure storage and transaction methods is a topic that every encryption user needs to pay attention to.
Next, we will summarize several key security suggestions from these cases, hoping to provide practical reference for everyone when managing digital assets, help reduce risks and avoid becoming the next victim.
1) Choose a reputable platform
Choosing a CEX or platform with a good security record and transparent disclosure of security measures is the first step in protecting personal assets.
2) Use cold storage to protect assets
Storing important digital assets in cold wallets is an important means to prevent hacker attacks.
3) Enable two-factor certification (2FA)
By binding mobile phones, email or dedicated validators, users can add an extra level of security when logging in, effectively preventing unauthorized access to accounts. Regular inspection and monitoring of account activities is an effective means to detect suspicious transactions and potential threats in a timely manner.
5) Diversify investment and reduce risks
Dispersing assets across multiple platforms or wallets can spread risk. For example, users can keep most of their assets in cold wallets and use a small amount of money for daily transactions, or spread it among different trustworthy CEXs to reduce the overall losses caused by problems with a single platform.
6) Trust
The most important feature of encrypted assets is that they can be verified. Don’t default to trust any third party to ensure your encryption security, including the software and hardware provided by wallet developers. At the same time, by default, personal networked devices are treated as “non-fully secure devices”. Operate, be sure to personally verify that every transaction information you submit and sign is accurate.
03. Summary
It can be said that security prevention is not only a response to problems, but also a proactive strategic layout. Cryptographic asset management is not only to deal with immediate risks, but also to ensure long-term stable development. Only by cultivating daily safety habits, gradually strengthening protective capabilities, and preventing risks at every link can we effectively minimize risks.



